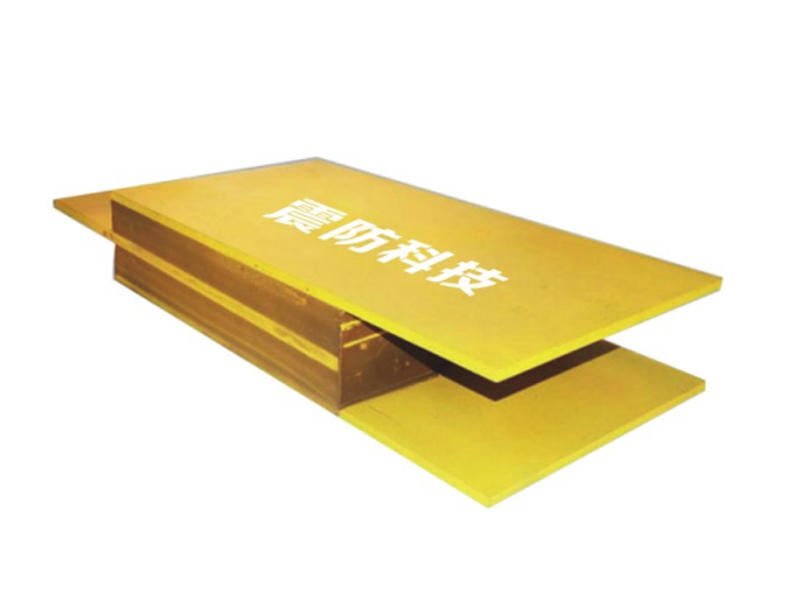
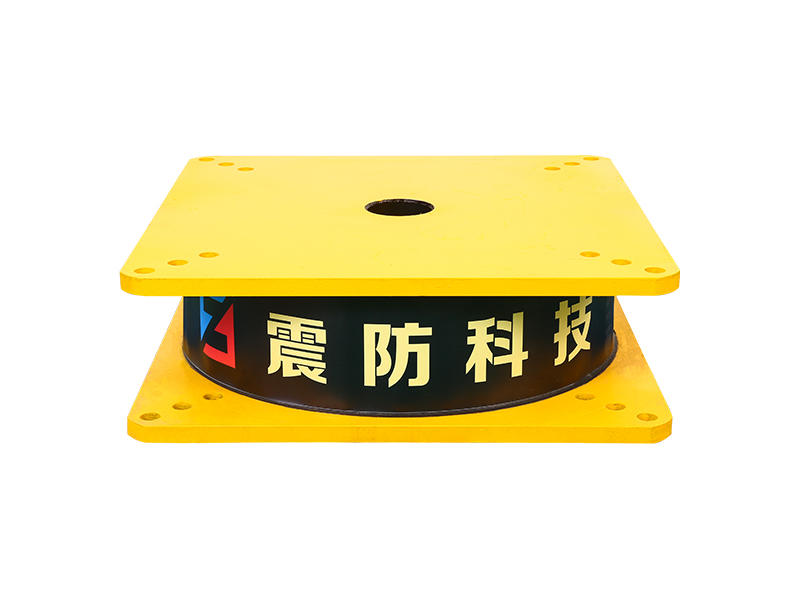
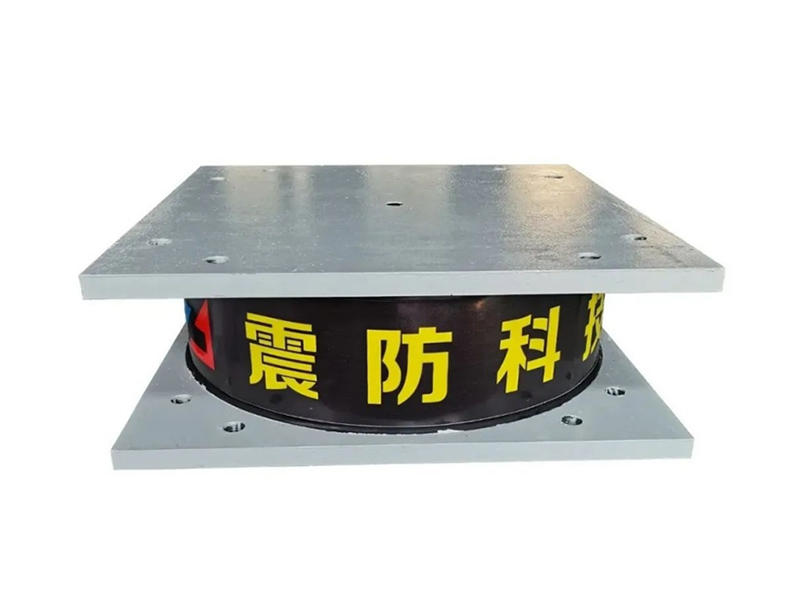
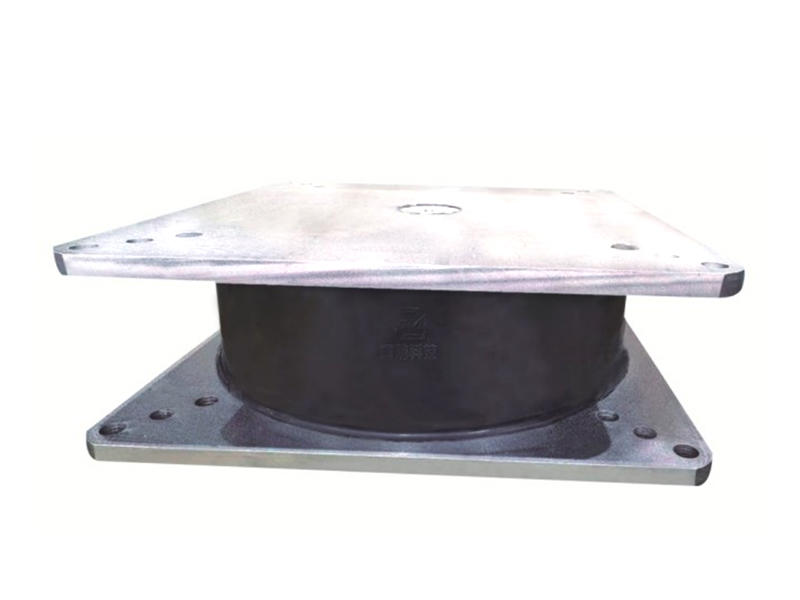
In the quest to fortify buildings against the devastating impacts of earthquakes, engineers and researchers have been relentless in their pursuit of innovative solutions.
Viscoleastic dampers, also known as VEDs, have emerged as a game-changing technology in seismic resilience. This article explores the concept and benefits of integrating viscoleastic dampers into building structures, showcasing how these advanced devices significantly enhance structural stability and mitigate earthquake-induced damage.
Understanding Viscoleastic Dampers
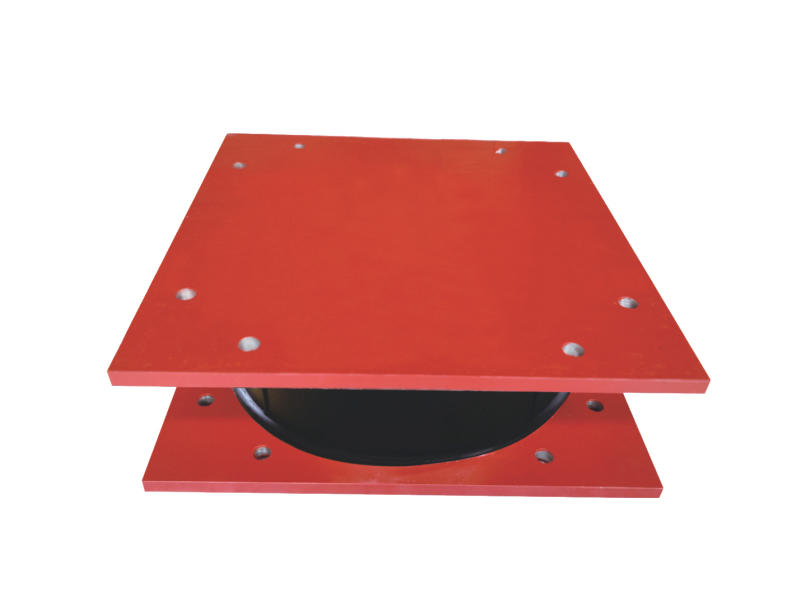
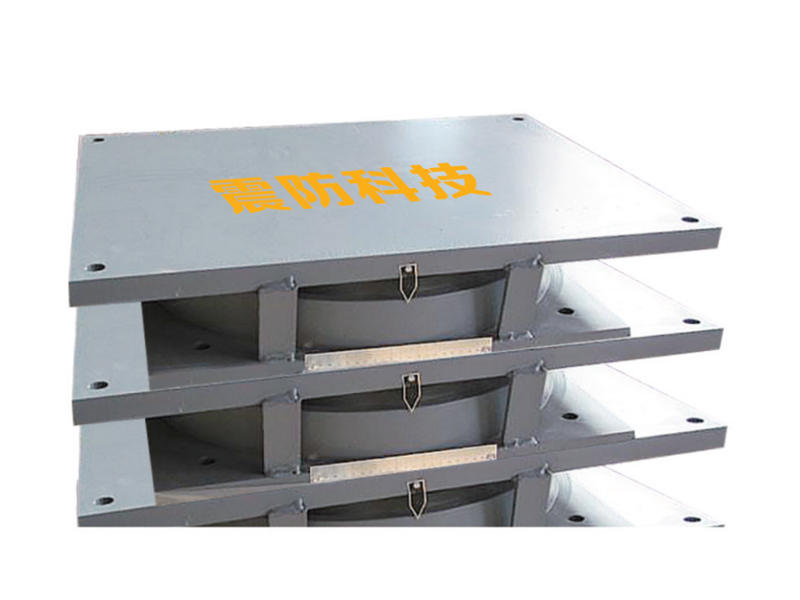
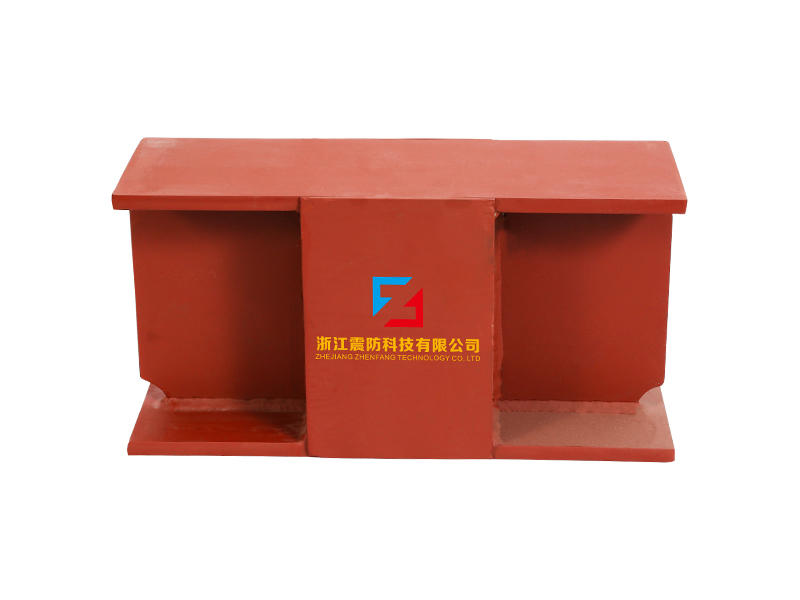
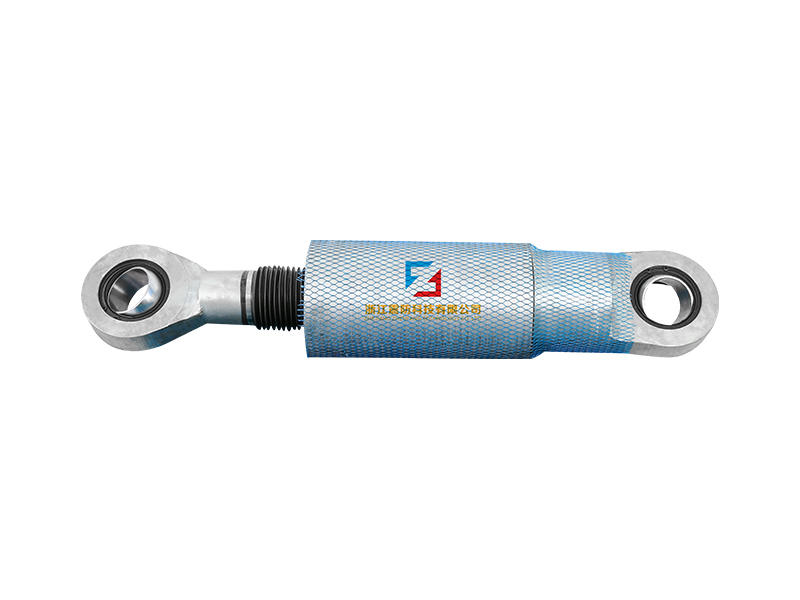
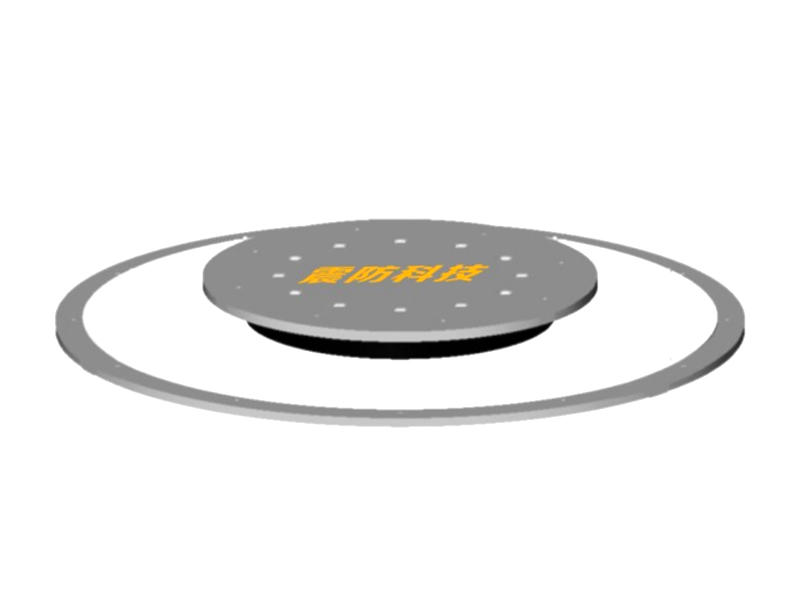
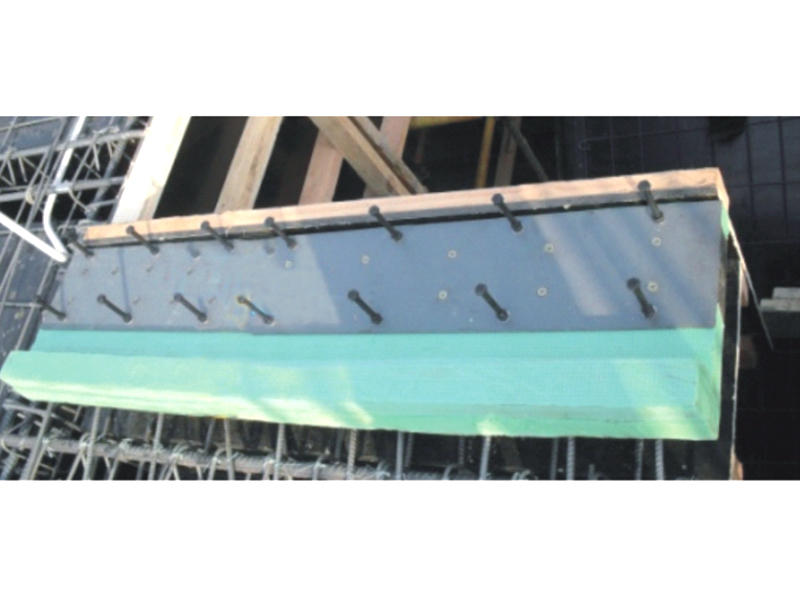
Viscoleastic dampers are seismic-resistant devices designed to absorb and dissipate energy during ground shaking. They consist of viscoelastic materials, typically polymers or elastomers, sandwiched between metal plates. The unique properties of these materials allow them to exhibit both viscous and elastic behavior, making them ideal for mitigating the effects of seismic forces on buildings.
How Viscoleastic Dampers Work
During an earthquake, the ground motion induces lateral forces on a building. These forces cause lateral movement, leading to structural deformations and potential damage. Viscoleastic dampers are strategically installed in the building's structure to counteract these lateral forces. When subjected to seismic loads, the viscoelastic material in the damper undergoes viscoelastic deformation, effectively converting the kinetic energy of the earthquake into heat. This energy dissipation mechanism absorbs and reduces the seismic forces acting on the building, protecting it from severe damage.
Benefits of Viscoleastic Dampers
a. Enhanced Structural Resilience: By absorbing and dissipating seismic energy, viscoleastic dampers significantly reduce the building's lateral displacements and deformations. This enhanced resilience ensures that the structure can withstand strong seismic events with minimal damage.
b. Controlled Building Response: Viscoleastic dampers provide a controlled response to seismic forces, ensuring that the building's movement remains within safe limits. This prevents excessive swaying, which could lead to structural failure or discomfort for occupants during an earthquake.
c. Retrofitting Existing Structures: One of the most remarkable advantages of viscoleastic dampers is their applicability to existing buildings. Through careful retrofitting, engineers can upgrade older structures with VEDs, significantly improving their seismic performance without the need for extensive reconstruction.
Integration into Various Building Types
Viscoleastic dampers can be integrated into a wide range of building types, including commercial complexes, residential towers, bridges, and even cultural heritage sites. Their versatility and adaptability make them a preferred choice for enhancing the seismic resilience of diverse structures.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Several regions prone to seismic activity have successfully implemented viscoleastic dampers in their building designs. Notable case studies from earthquake-prone areas, such as Japan and California, have demonstrated the effectiveness of VEDs in reducing structural damage and protecting lives during major seismic events.
Future Prospects and Advancements
As research and technology in seismic engineering continue to progress, there is a growing interest in refining and optimizing viscoleastic dampers. Ongoing studies focus on enhancing the durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness of these devices to ensure their widespread adoption in the construction industry.
In a world where seismic events pose an ever-present threat to buildings and infrastructure, viscoleastic dampers represent a beacon of hope for enhanced structural stability. Through their ability to absorb and dissipate seismic energy, these innovative devices play a pivotal role in safeguarding buildings and their occupants during earthquakes. As engineers continue to embrace and refine viscoelastic damper technology, we can expect a future where structures stand resilient in the face of nature's most powerful forces, providing safer and more secure urban environments for generations to come.