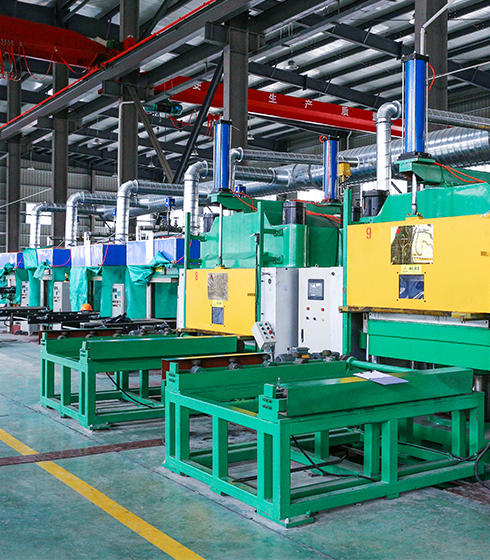


Zhejiang Earthquake Prevention Technology Co., Ltd committed to product research and development, technical consultation, structural analysis and design, production, guide installation and replacement. Professional in the field of building seismic isolation products and Earthquake Shock Absorbers products in China. We have a modern industrial manufacturing production base with a total area of more than 10,800 square meters. The company has more than 50 sets of production equipment. Production capacity: more than 10,000 sets of rubber isolation bearings per year.
In the realm of seismic engineering and infrastructure resilience, the concept of base isolation using low damping lead rubber bearings (LRBs) has gai...
Apr 26,2024
In the realm of earthquake engineering and structural resilience, low damping lead rubber bearings (LRBs) have emerged as critical components in mitig...
Apr 19,2024
In the realm of earthquake engineering, a groundbreaking technology is emerging to redefine seismic resilience: the low damping lead rubber bearing (L...
Apr 12,2024
In the realm of structural engineering and seismic resilience, lead rubber bearings (LRBs) stand out as crucial components that mitigate the impact of...
Apr 05,2024
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTE
Add: No. 359 Guangming West Road, Sanmen County, Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
International Trade Manager: Madison
Tel/Whatsapp:+86-17857335842
Copyright © Zhejiang Earthquake Prevention Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
