The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEAs global infrastructure development surges, the demand for advanced seismic protection technologies is also on the rise. Among the talked-about innovations in recent civil engineering projects is the High Damping Rubber Bearing (HDRB)—a key solution changing how buildings and bridges are protected against earthquakes. Used in both new constructions and seismic retrofits, HDRBs are increasingly becoming the good choice for engineers seeking cost-effective and reliable base isolation systems.
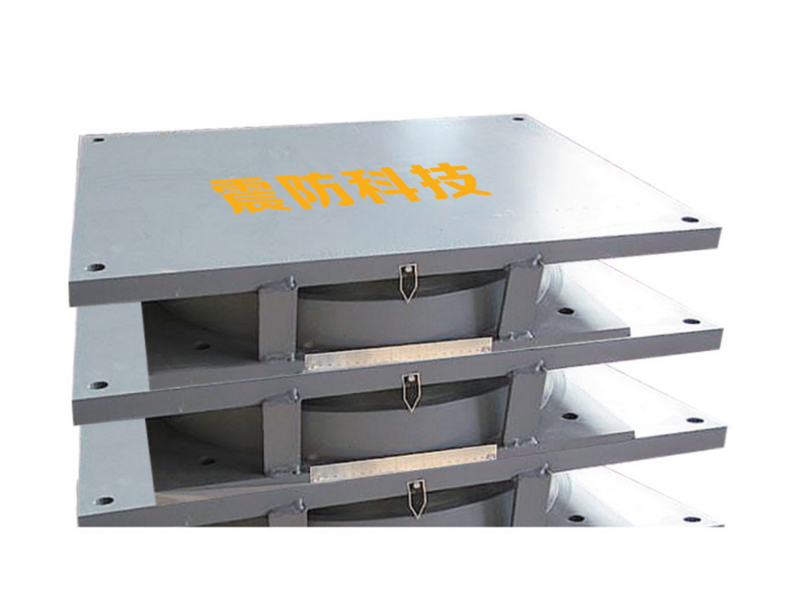
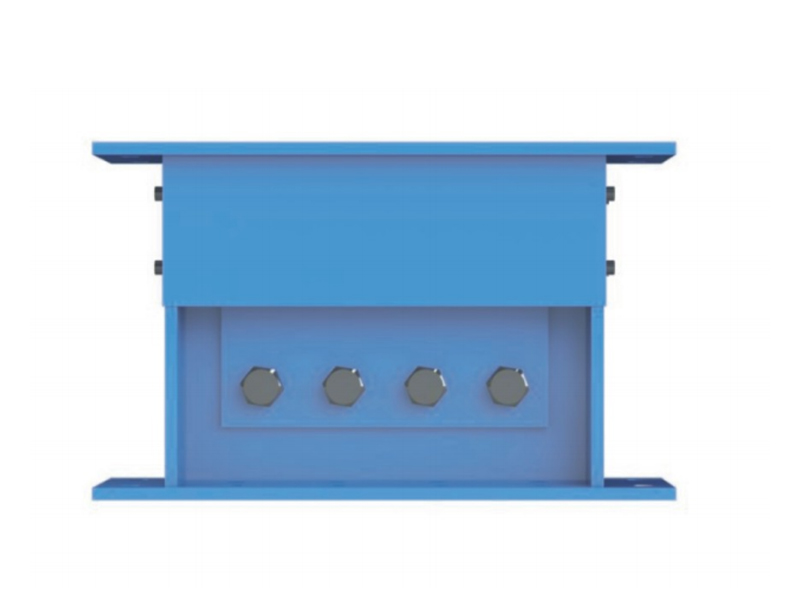
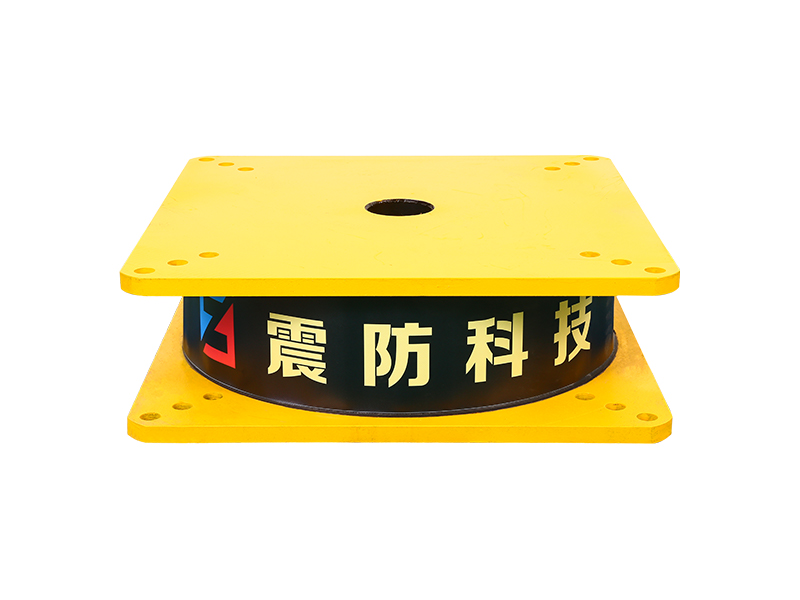
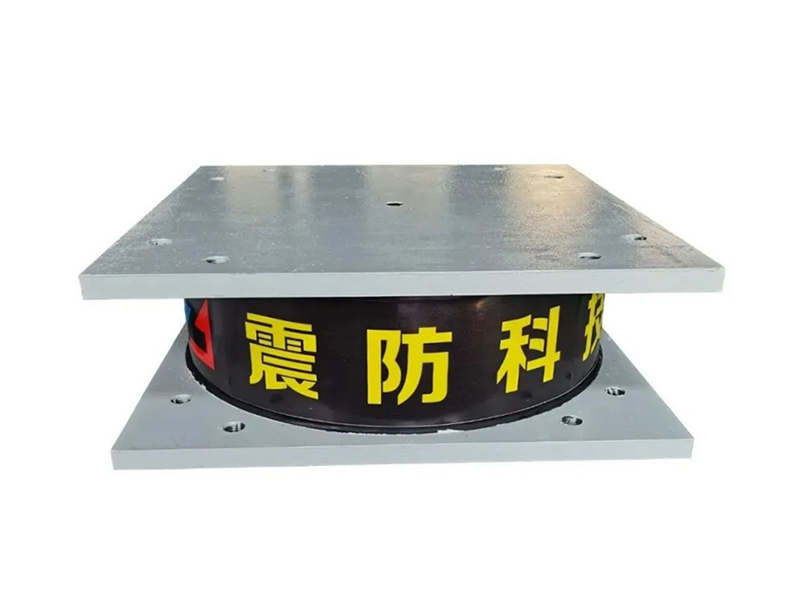
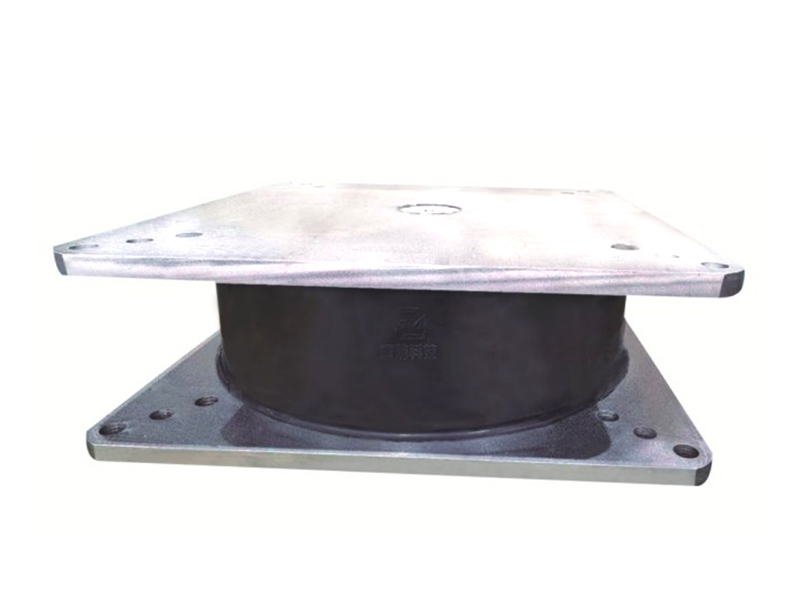
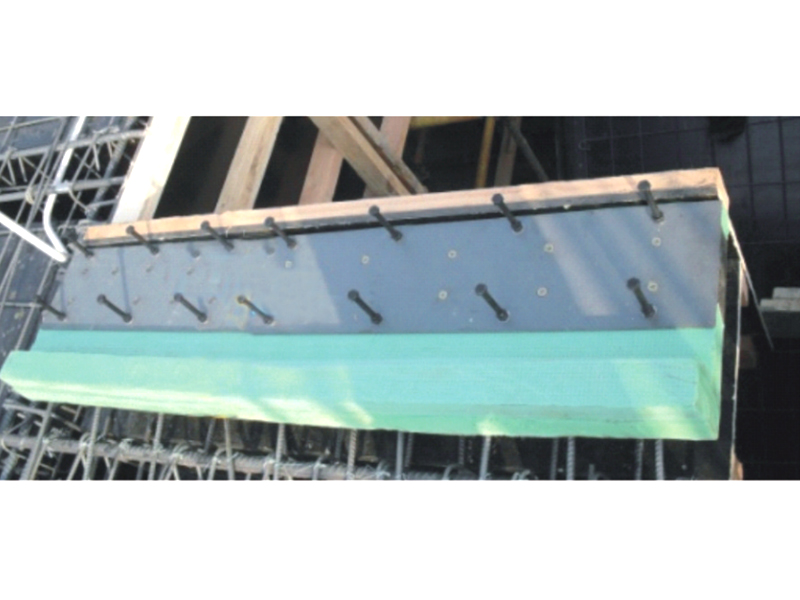
The High Damping Rubber Bearing is a type of seismic isolator that consists of alternating layers of rubber and steel plates, with specially formulated rubber compounds providing energy dissipation through hysteresis. Unlike conventional elastomeric bearings, HDRBs offer the dual function of isolating structures from ground motion while also damping vibratory energy, thus significantly reducing structural damage during seismic events.
With urbanization expanding in seismic-prone regions across Asia, North America, and parts of Europe, demand for the High Damping Rubber Bearing has spiked. Recent announcements from major infrastructure projects, including transportation hubs and high-rise commercial complexes, have highlighted the role of HDRBs in meeting stringent earthquake resilience codes.
In Japan, a nation long recognized for its advanced earthquake engineering, the High Damping Rubber Bearing has become an essential component in both public infrastructure and private development. A Tokyo-based engineering firm recently completed retrofitting a 30-story office tower with HDRBs, enhancing the building’s seismic performance without interrupting daily operations. The project is now being cited as a benchmark for seismic retrofitting in densely populated urban centers.
The benefits of the High Damping Rubber Bearing extend beyond earthquake protection. Due to their ability to absorb and dissipate energy, HDRBs also reduce long-term structural fatigue caused by minor tremors and environmental vibrations. This makes them proper for not only earthquake-prone areas but also regions with frequent ground or traffic-induced vibrations.
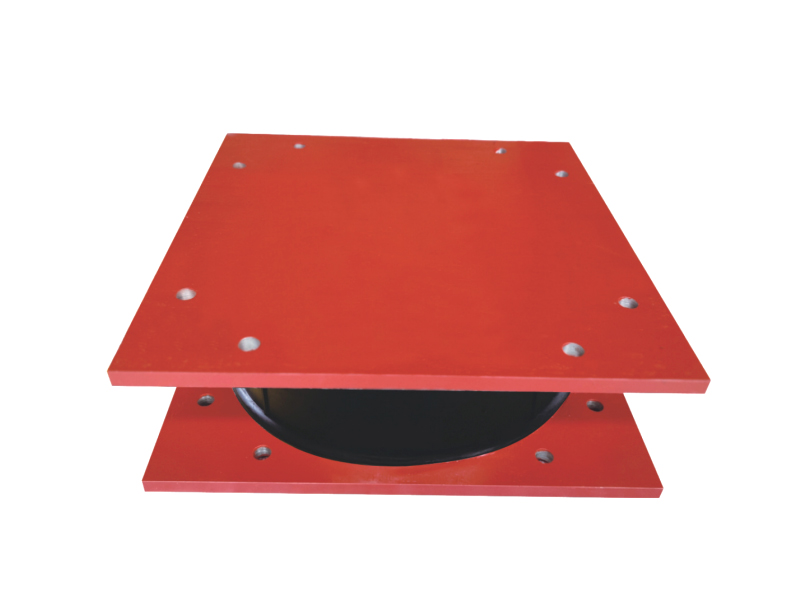

According to a recent market research report, the global market for High Damping Rubber Bearing systems is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% through 2030. Industry innovators such as Bridgestone, Sumitomo Rubber Industries, and Maurer SE are investing heavily in R&D to develop next-generation HDRBs that offer even higher performance with reduced size and cost.
Engineers and policymakers are increasingly aware of the benefits of HDRBs, particularly in light of recent seismic events that have exposed vulnerabilities in traditional building designs. A 2024 earthquake in southern Turkey, for instance, caused significant damage to older buildings lacking seismic isolation, while structures equipped with High Damping Rubber Bearing technology fared notably better.
“Adopting High Damping Rubber Bearing technology in critical infrastructure is not just about meeting compliance—it's about saving lives,” says Dr. Elena Tanaka, a structural engineer specializing in seismic isolation. “It allows buildings to remain operational immediately after an earthquake, which is vital for hospitals, data centers, and emergency services.”
Municipal governments are taking note. In California, where earthquake readiness is a top priority, state building codes are being updated to recommend or require the use of seismic isolators like HDRBs in certain types of public buildings. Similar regulatory trends are being observed in New Zealand and Chile, both countries with active seismic zones.
As more developers realize the long-term cost benefits and life-saving potential of the High Damping Rubber Bearing, adoption is expected to accelerate. The up-front investment is often offset by lower insurance goods, extended building lifespan, and reduced repair costs following a seismic event.
In the academic sphere, universities and research institutions are contributing to the growing body of knowledge surrounding HDRBs. Recent studies have explored the customization of High Damping Rubber Bearing materials to improve temperature stability and lifespan, opening up new possibilities for installations in harsh environments.