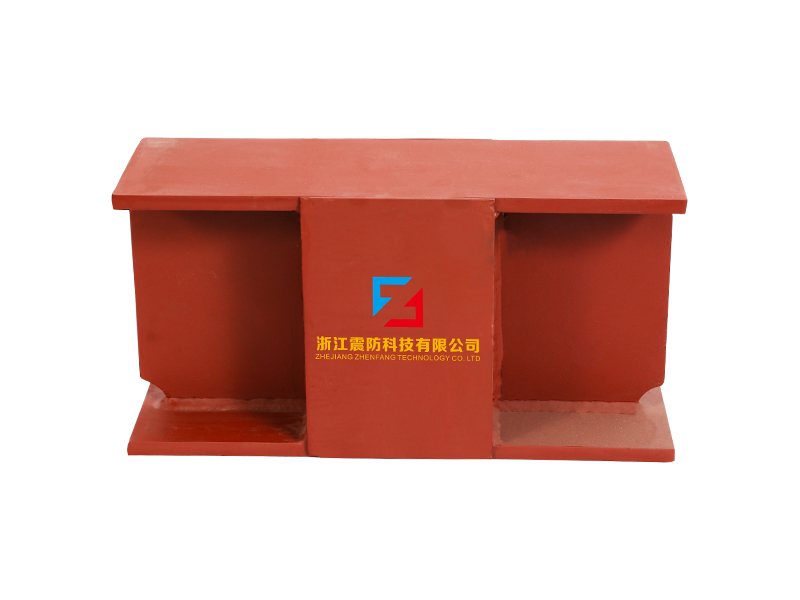
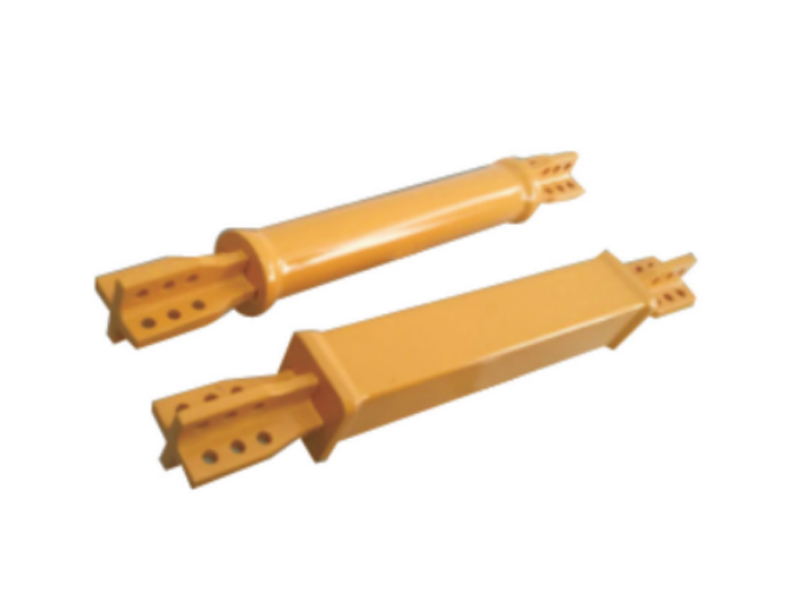
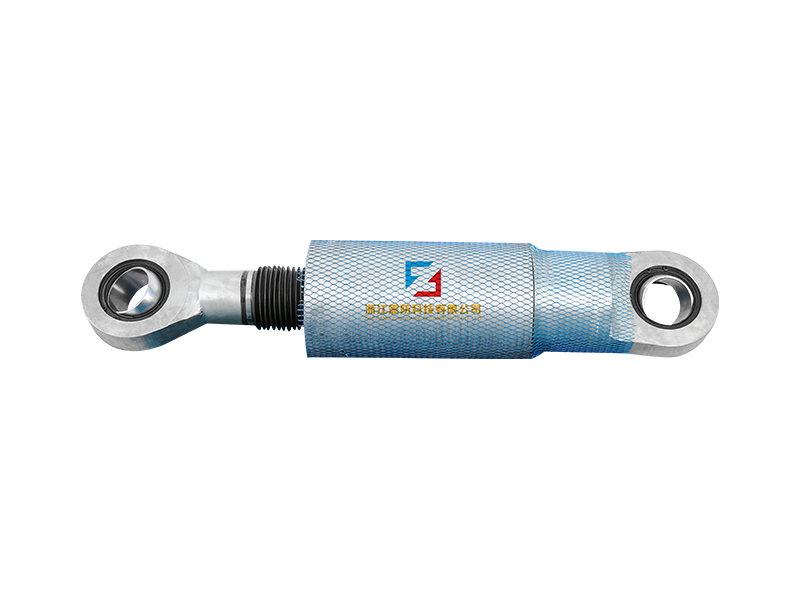
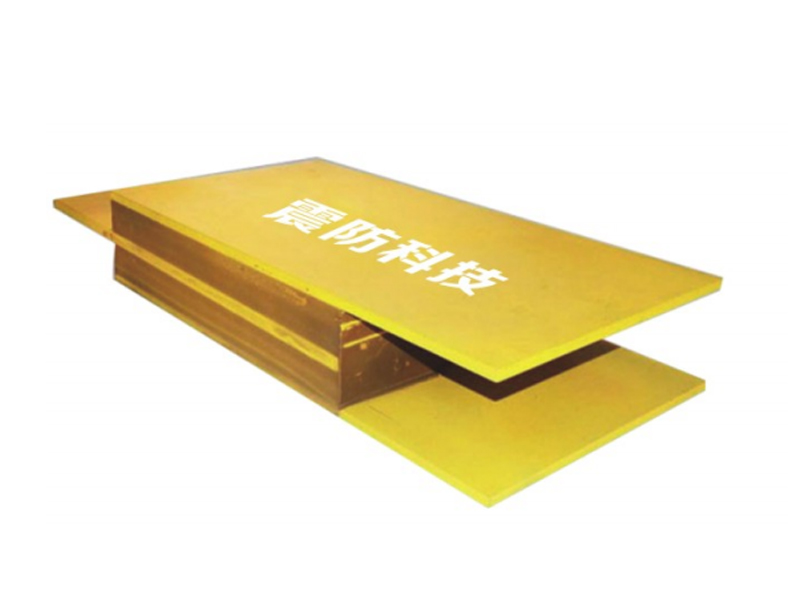
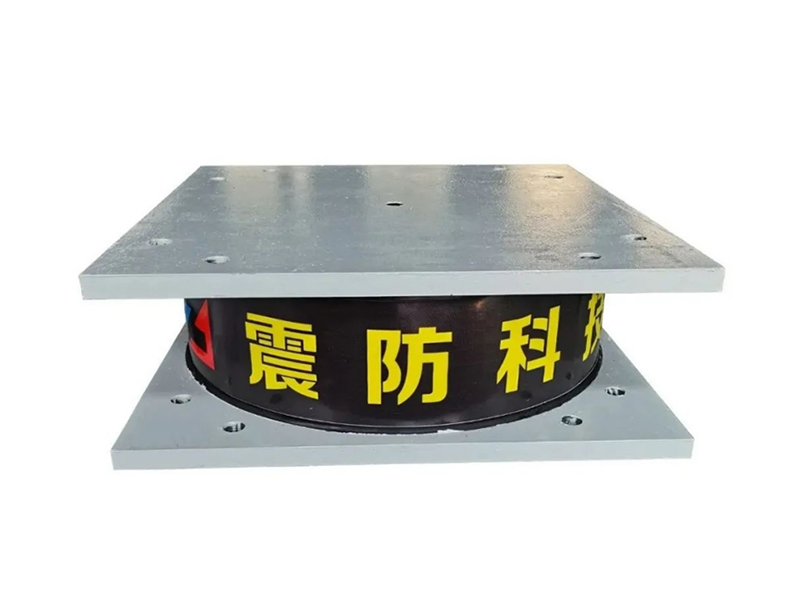
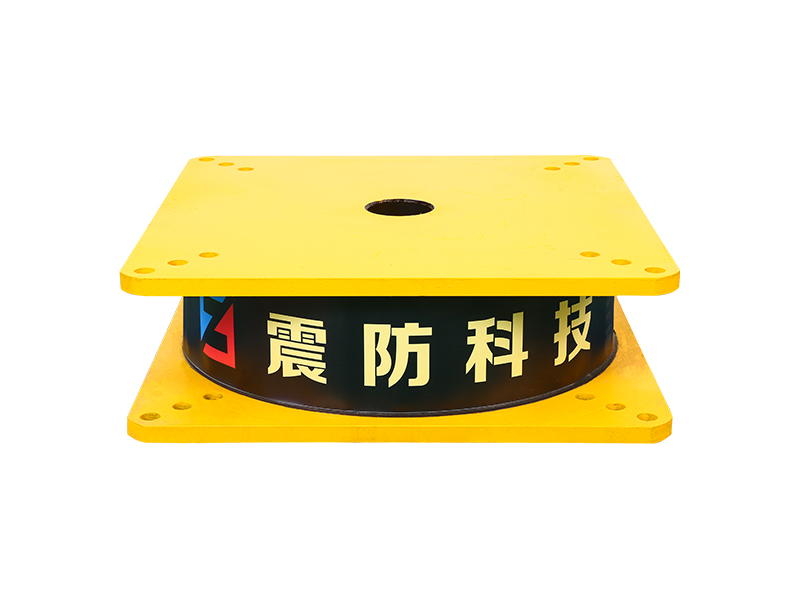
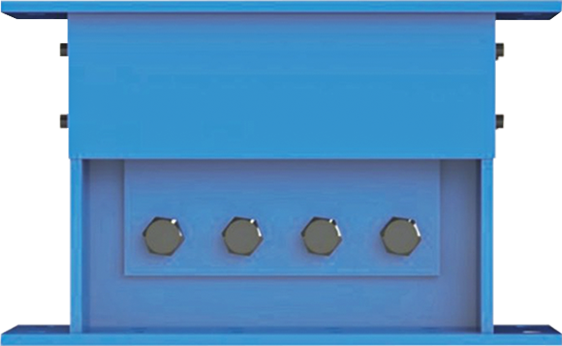
The viscoelastic damper is a rigid viscous damping device. There are three types of load-deformation hysteresis curves: linear, deformation-softening, and deformation-hardening. Its mechanical model includes a model applying fractional differential constitutive relation and a model combining spring and damper, and its damping force is related to velocity and displacement. The shape of the damper includes a plane type and a cylinder type. The viscoelastic damper is made of viscoelastic damping material and constraining steel plate alternately superimposed and bonded. In addition to viscoelastic damping material, there are constraining steel plate and adhesive layer. The latter two materials hardly consume energy, so The loss factor of viscoelastic dampers is smaller than that of viscoelastic materials. The mechanical properties of viscoelastic dampers cannot be completely equal to those of viscoelastic damping materials. Under the action of external force, the deformation of viscoelastic dampers is the sum of the deformations of viscoelastic damping materials, steel plates and adhesives.
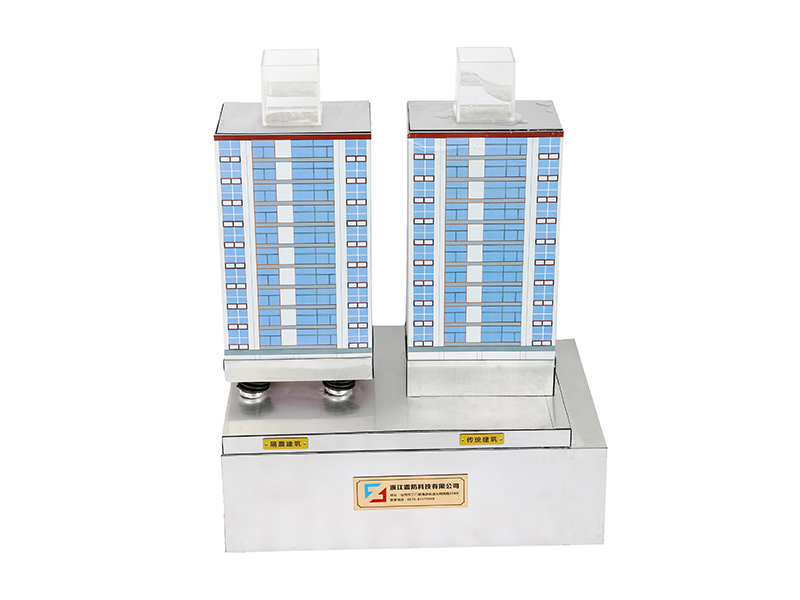
Applications of Viscoelastic Dampers:Viscoelastic dampers (VED) are generally located in positions that can produce relative deformation, such as diagonal bracing, herringbone bracing, beam-column joints, truss lower chords or between adjacent buildings. When displacement occurs between structural layers, viscoelastic damping It will produce shear hysteretic deformation, dissipate the input vibration energy and reduce the vibration response of the structure.
Viscous damper classification and selection:
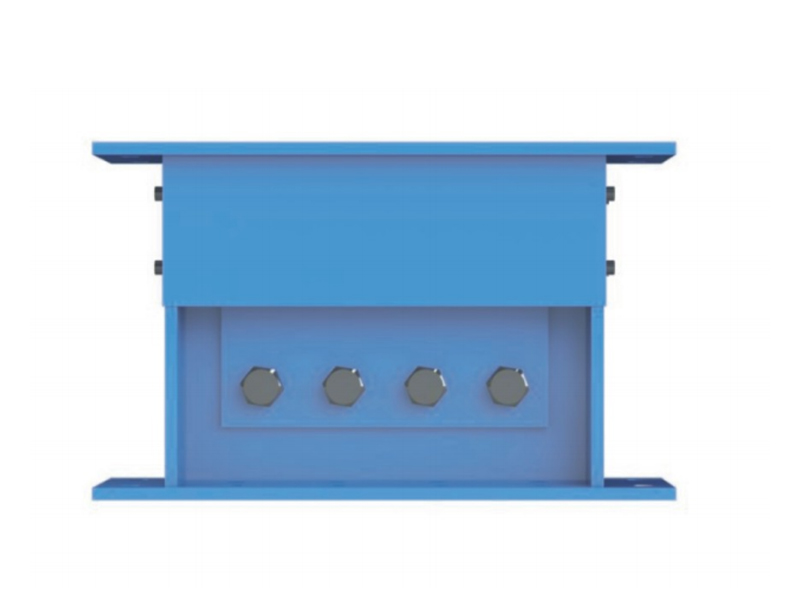
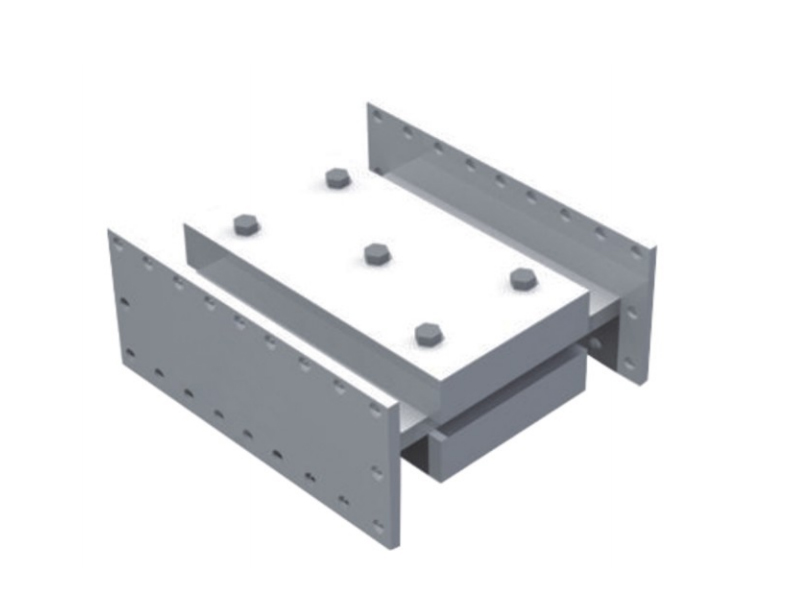
The wall panel viscoelastic damper is composed of upper steel plate, lower steel plate and viscoelastic material filled between them. When the building undergoes shear deformation in the horizontal direction, the upper and lower steel plates of the viscoelastic damper will move with each other, which will drive the viscoelastic material to undergo shear deformation to dissipate the energy of the land administration.


 English
English 日本語
日本語 русский
русский 简体中文
简体中文