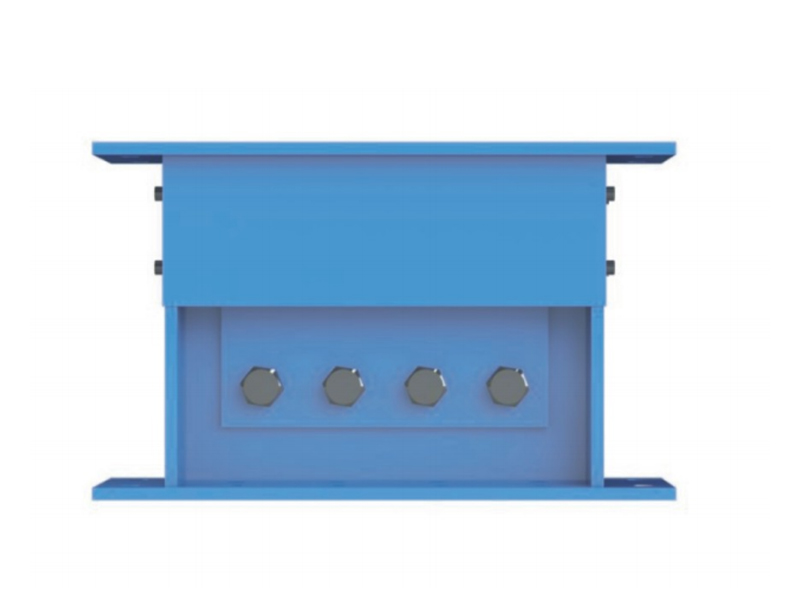
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEIn earthquake-prone regions, safeguarding buildings against the destructive power of seismic events is a top priority for engineers and architects alike. Traditional building methods often struggle to protect structures from the intense shaking caused by earthquakes, leading to catastrophic damage and loss of life. To address this challenge, seismic isolation bearings have emerged as a game-changing solution, providing an innovative way to reduce the impact of seismic forces on buildings. These advanced bearings offer both cost-effective and highly reliable protection, making them increasingly popular in earthquake-resistant design.
What Are Seismic Isolation Bearings?
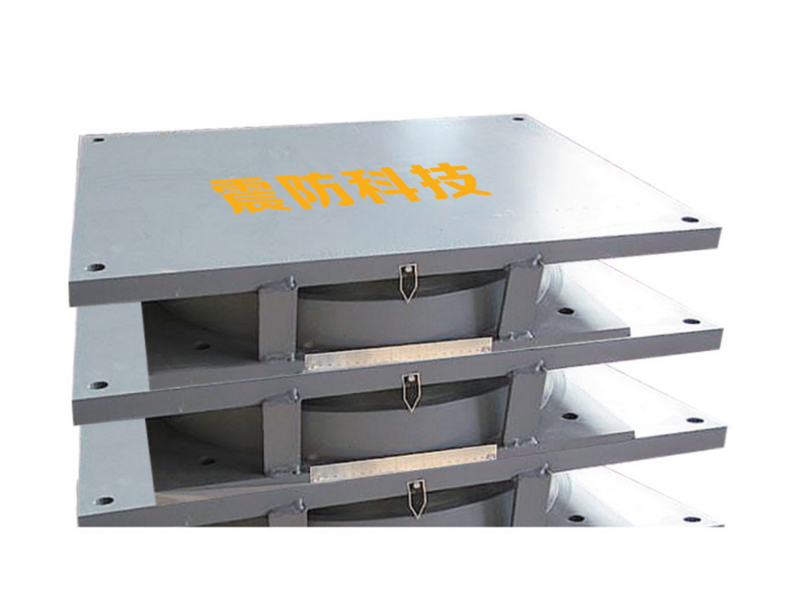
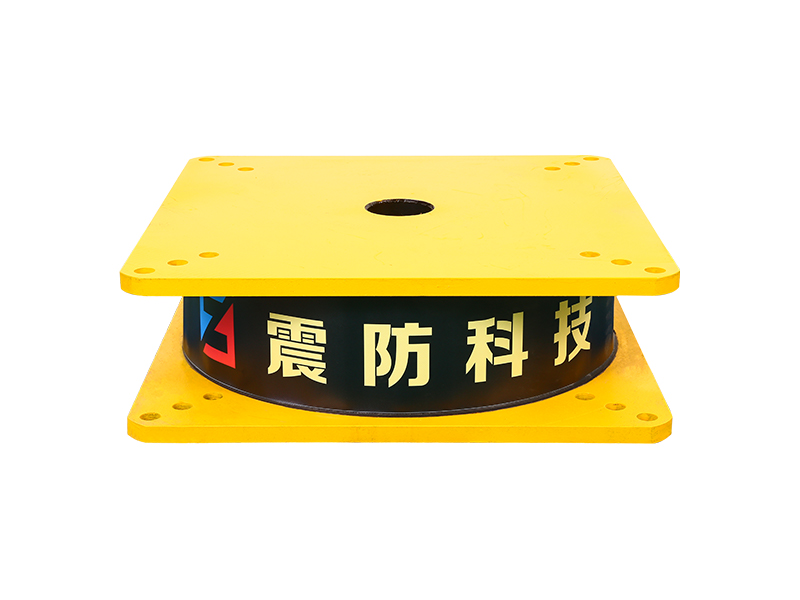
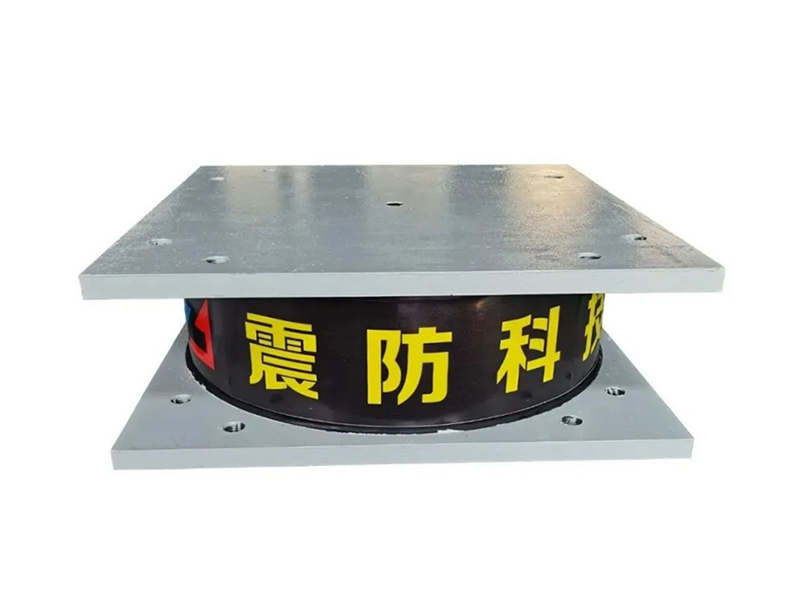
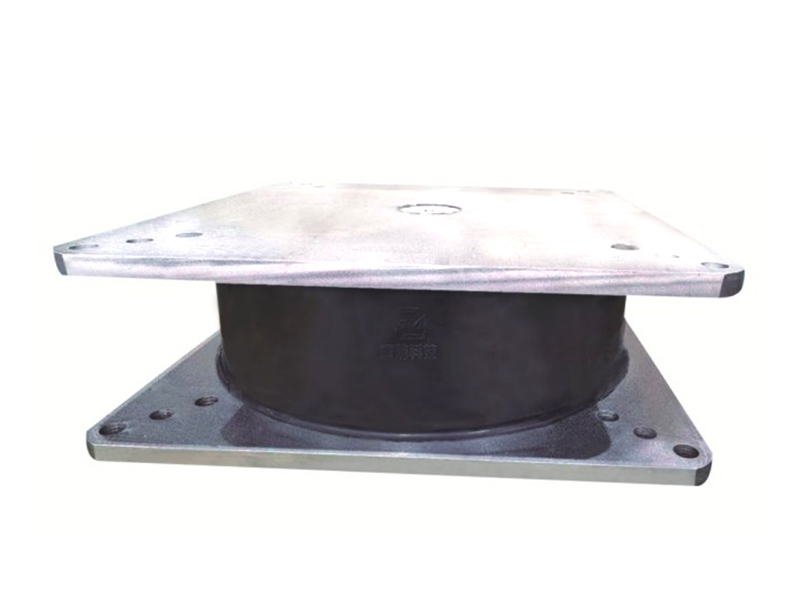
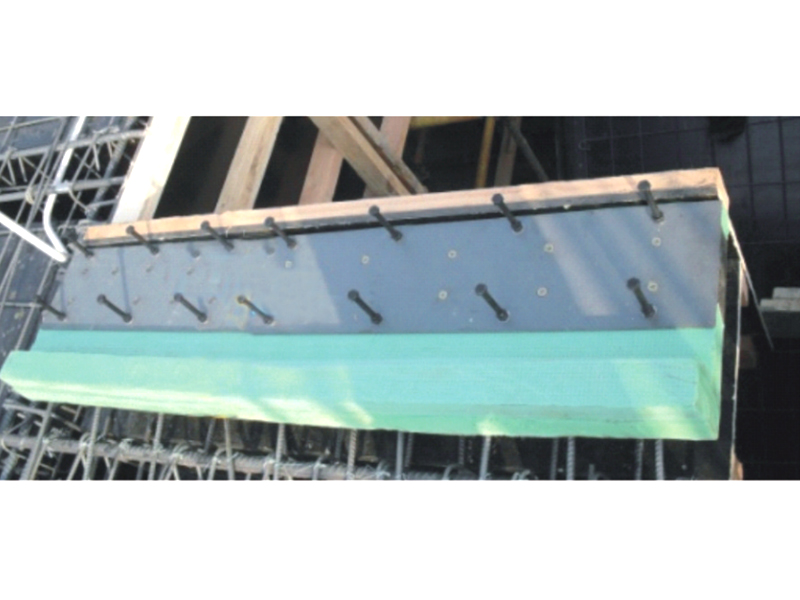
Seismic isolation bearings, also known as base isolators, are mechanical devices used in the foundations of buildings to absorb and dissipate seismic energy. The bearings are typically made from a combination of elastomers (rubber), steel, and sometimes other advanced materials, engineered to allow for controlled movement during an earthquake. Installed between a building's foundation and superstructure, seismic isolation bearings enable the structure to move independently from the ground motion, reducing the transfer of seismic forces to the building.
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves travel through the earth, causing the ground to shake. Without seismic isolation, this shaking is directly transferred to the structure, potentially causing severe damage. Seismic isolation bearings absorb and dissipate this energy, allowing the building to shift and move in response to the seismic waves while keeping the upper structure stable and intact.
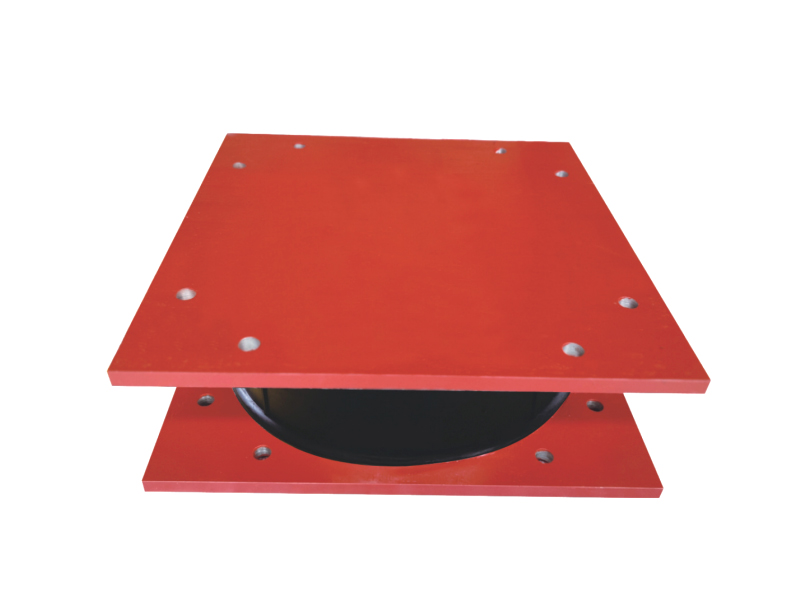

The primary function of seismic isolation bearings is to decouple the building's foundation from the ground motion. This isolation is achieved through the flexible and resilient properties of the materials used in the bearings, allowing the building to absorb and dissipate the energy of an earthquake before it can cause any significant damage.
How Do Seismic Isolation Bearings Work?
Seismic isolation bearings work by acting as a cushion between the foundation and the building's superstructure. During an earthquake, the building moves independently of the ground, which helps reduce the amount of seismic energy that is transferred into the structure. These bearings are designed to deform under pressure, absorbing the seismic forces and allowing the building to flex in a way that reduces the intensity of shaking.
A typical seismic isolation bearing consists of alternating layers of rubber and steel. The rubber layers provide flexibility, enabling the bearing to deform when subjected to seismic forces, while the steel layers provide strength and stability. In some cases, additional materials such as lead or other energy-dissipating components may be incorporated to further enhance the bearing's performance.
The rubber layers in seismic isolation bearings act as a shock absorber, compressing and expanding in response to the seismic waves, while the steel plates offer vertical support, ensuring that the building remains stable despite horizontal movement. This combination of flexibility and strength allows the bearings to absorb and dissipate seismic energy effectively, preventing the ground motion from damaging the building.
Advantages of Seismic Isolation Bearings
The use of seismic isolation bearings in building design offers numerous advantages, making them an attractive option for earthquake-resistant construction. Some of the key benefits include:
Reduced Structural Damage: Seismic isolation bearings significantly reduce the amount of seismic energy that reaches a building's superstructure, thereby reducing the likelihood of structural damage. By allowing the building to move independently of the ground motion, these bearings help prevent cracks, collapses, and other forms of damage that would otherwise result from direct exposure to seismic forces.
Enhanced Safety: The primary goal of any earthquake-resistant design is to protect the lives of the building’s occupants. Seismic isolation bearings help enhance the safety of buildings by ensuring that they experience less movement during an earthquake. This minimizes the risk of injury and ensures that the building remains safe for its occupants throughout the event.
Cost-Effective Earthquake Protection: While seismic isolation bearings can initially be more expensive than traditional foundations, they can ultimately save money by reducing the need for extensive repairs and reconstruction after an earthquake. Buildings equipped with seismic isolation systems are less likely to experience significant damage, leading to lower repair costs and less downtime for businesses and residents.