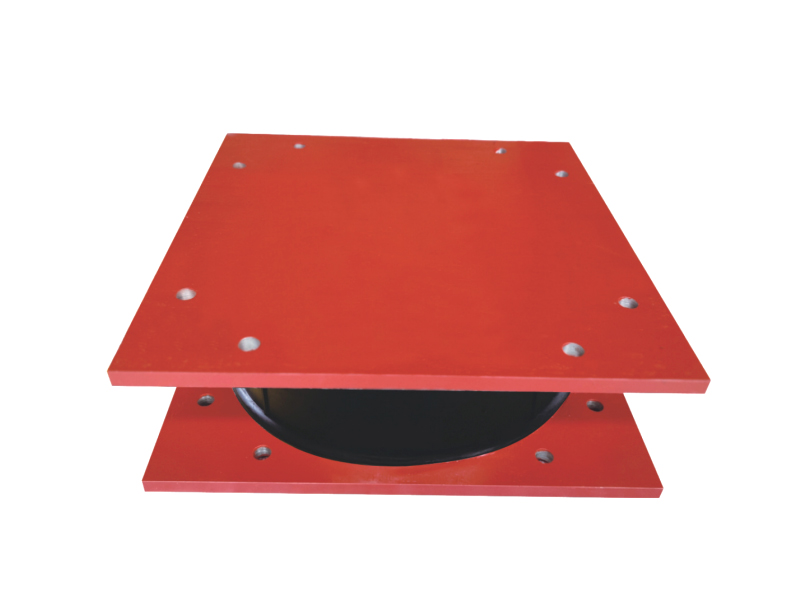
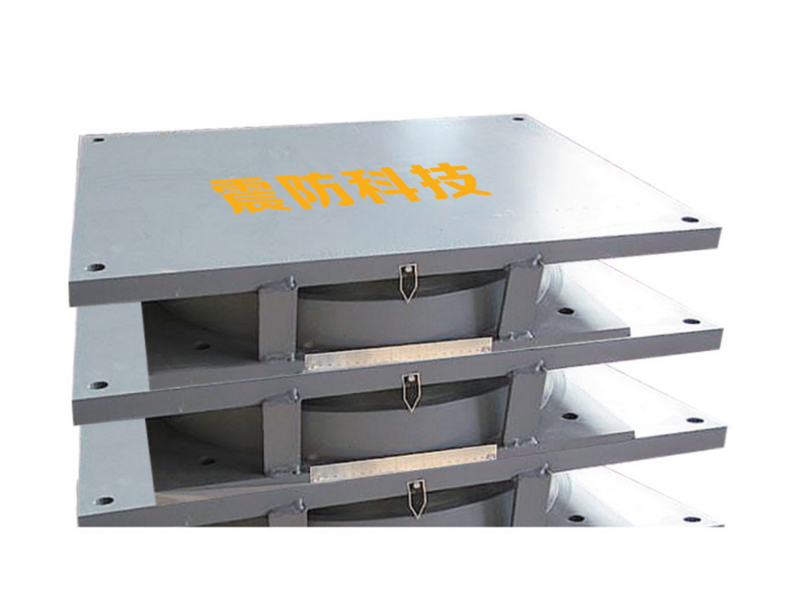
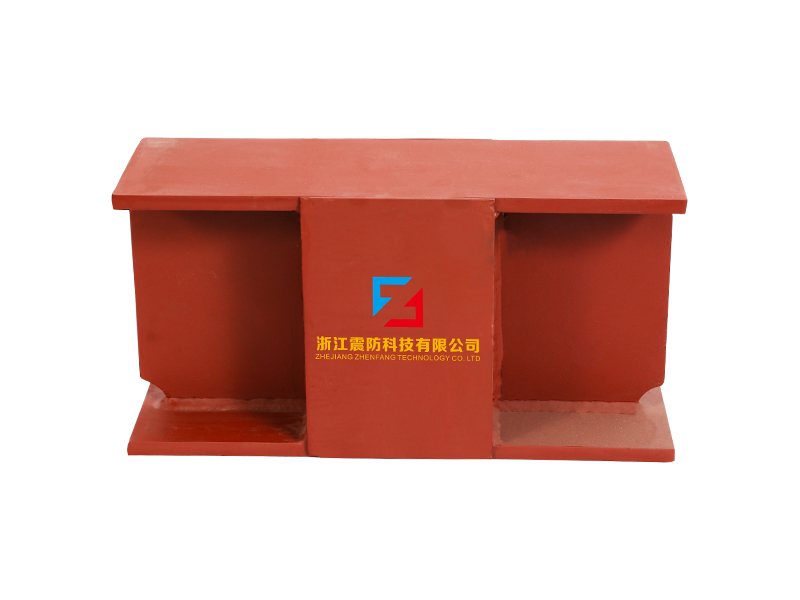
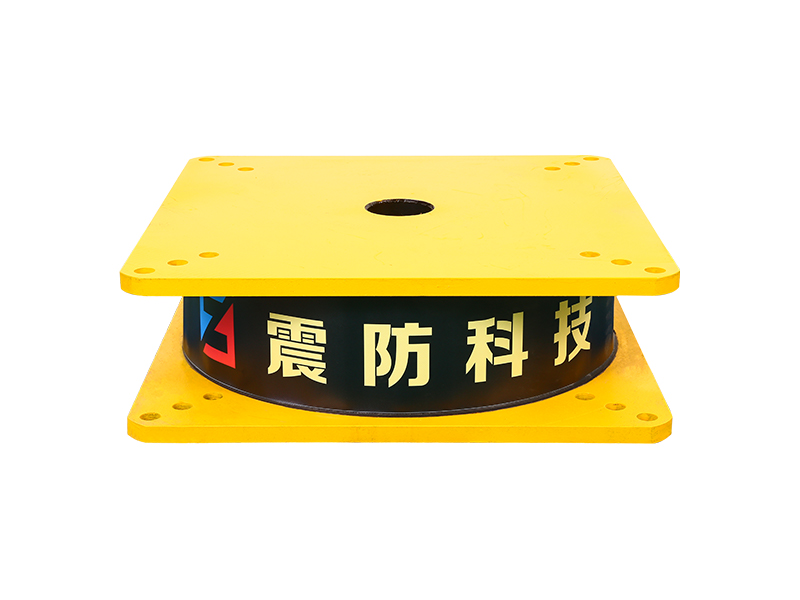
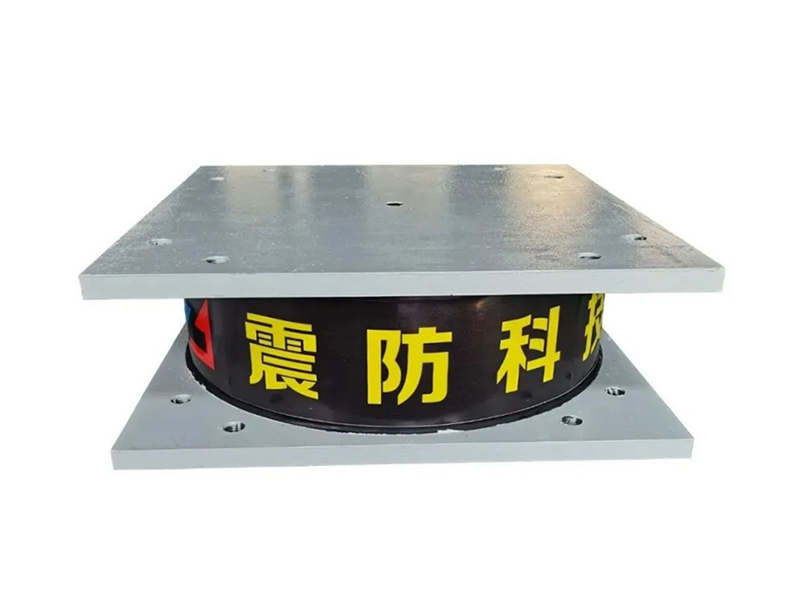
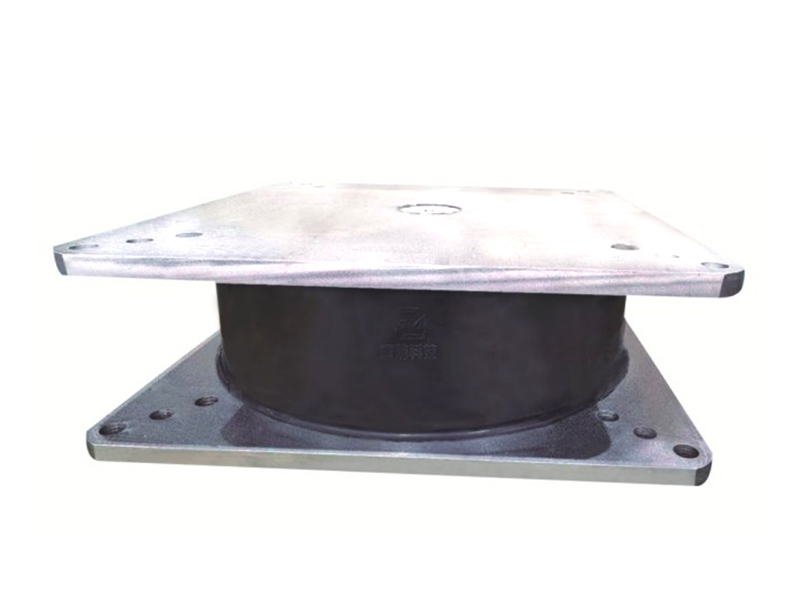
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEThe lead rubber bearing has emerged as a significant development in structural engineering, providing enhanced protection for buildings and infrastructure during seismic events. This specialized isolation system represents an important advancement in how structures manage seismic forces. The innovative design of the lead rubber bearing combines the durability of rubber with the energy-absorption qualities of lead, creating a component that can substantially improve a structure's response to earthquake forces.
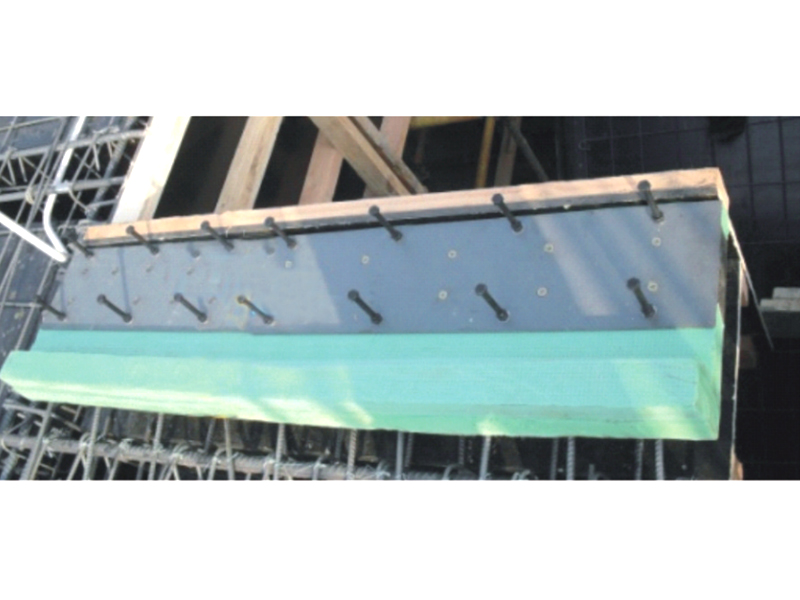
The fundamental construction of a lead rubber bearing involves multiple layers of rubber and steel plates bonded together, with a solid lead core inserted at the center. This configuration allows the lead rubber bearing to perform two crucial functions simultaneously. The rubber and steel layers provide flexibility for the structure to move horizontally during ground motion, while the lead core dissipates seismic energy through its ability to deform and then return to its original shape. This combination makes the lead rubber bearing an effective solution for managing the complex forces generated during earthquakes.
Engineering applications for the lead rubber bearing span multiple sectors of construction. Civil engineers incorporate these isolation devices beneath bridges, where they help protect the structure from ground movements. Building designers install lead rubber bearing systems at the foundation level of hospitals, emergency response centers, and other critical facilities that must remain operational after seismic events. The implementation of lead rubber bearing technology allows structures to withstand ground motions that might otherwise cause significant damage to conventional buildings.
The performance characteristics of the lead rubber bearing make it suitable for various geographic regions with different seismic risk profiles. In areas with moderate seismic activity, the lead rubber bearing provides an additional safety margin that can prevent structural damage and protect occupants. For regions experiencing more significant seismic events, structures equipped with lead rubber bearing systems have demonstrated an improved ability to maintain structural integrity during and after earthquakes. The versatility of the lead rubber bearing design allows engineers to customize the specifications based on specific project requirements and local seismic conditions.
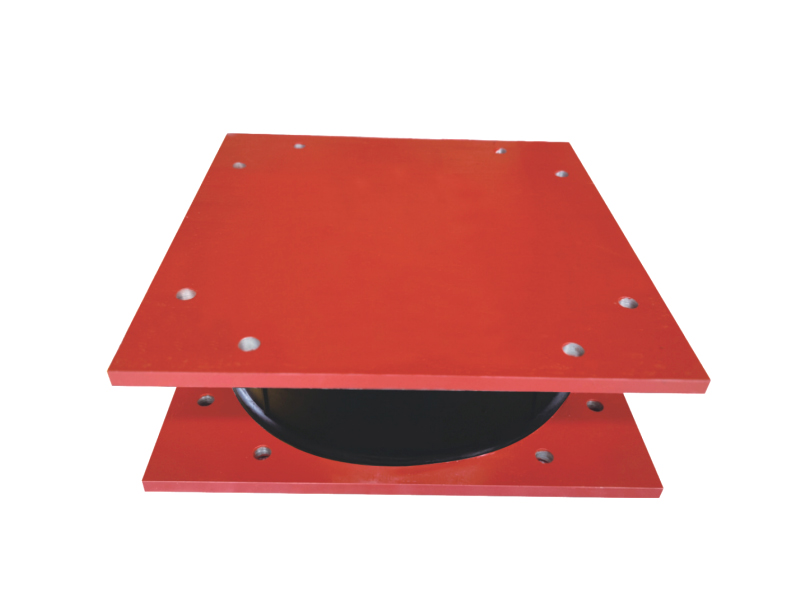

Research and development surrounding the lead rubber bearing continues to advance its capabilities. Engineering teams conduct extensive testing on lead rubber bearing components to verify their performance under various load conditions. These tests help refine the manufacturing standards and design parameters for the lead rubber bearing, ensuring consistent quality and reliability. The ongoing development of the lead rubber bearing includes improvements to its durability, load-bearing capacity, and ability to perform over extended service periods.
The installation process for a lead rubber bearing requires specialized knowledge and careful planning. Construction teams must follow precise procedures when positioning these isolation devices to ensure proper alignment and load distribution. The integration of a lead rubber bearing system into a structural design typically involves coordination between architects, structural engineers, and construction specialists. This collaborative approach ensures that the lead rubber bearing performs its intended function within the overall structural system.
As structural engineering continues to evolve, the lead rubber bearing remains an important tool for enhancing seismic safety. The proven performance of this technology in actual seismic events has reinforced its value within the engineering community. The continued refinement of lead rubber bearing specifications and installation standards contributes to more resilient infrastructure worldwide. With ongoing research and practical application, the lead rubber bearing will likely play an increasingly important role in global efforts to create earthquake-resistant structures.