The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEAcross diverse sectors of industrial automation, machinery design, and structural engineering, a specialized component is gaining recognition for its ability to manage movement and absorb forces in a specific direction: the linear rubber bearing. Unlike traditional rotational bearings, this device is engineered to accommodate controlled linear displacement, shear forces, and vibrations along a single axis while providing restraint in other directions. The growing application of the linear rubber bearing highlights its value in enhancing performance, isolating vibration, and ensuring alignment in systems requiring precise, guided motion.
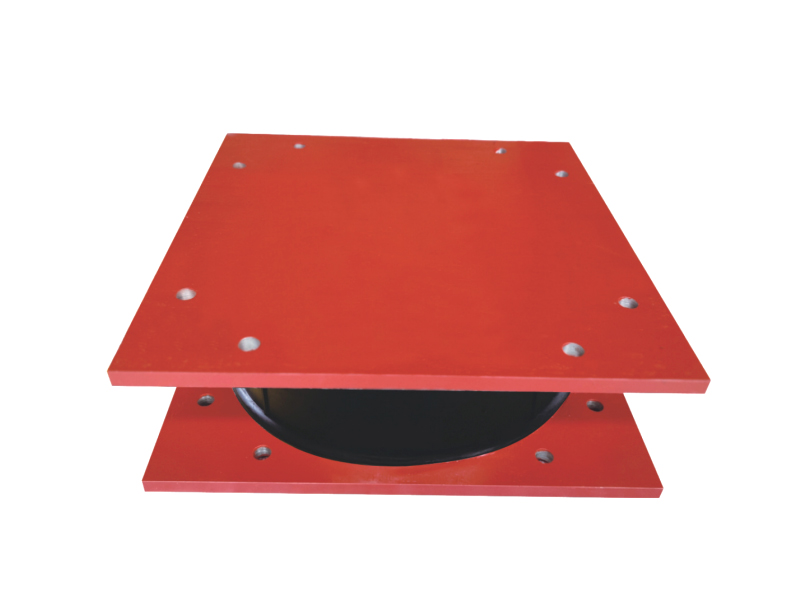
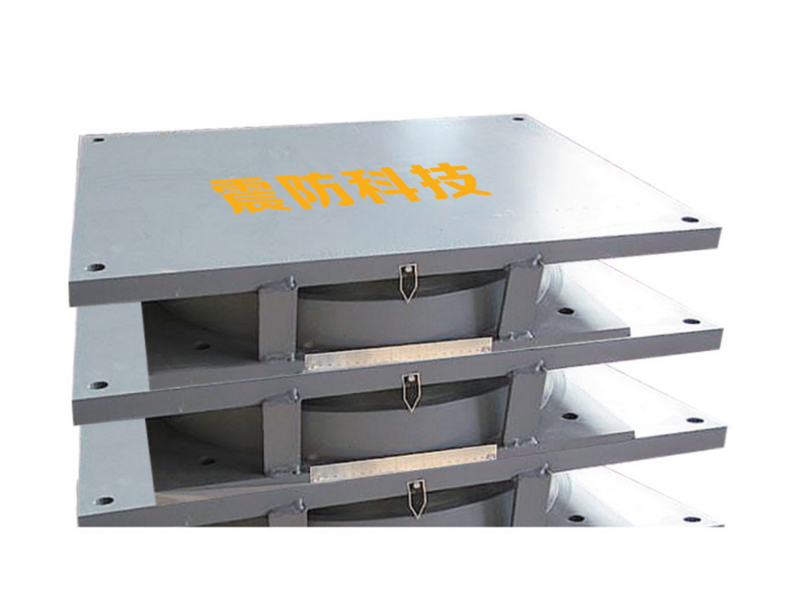
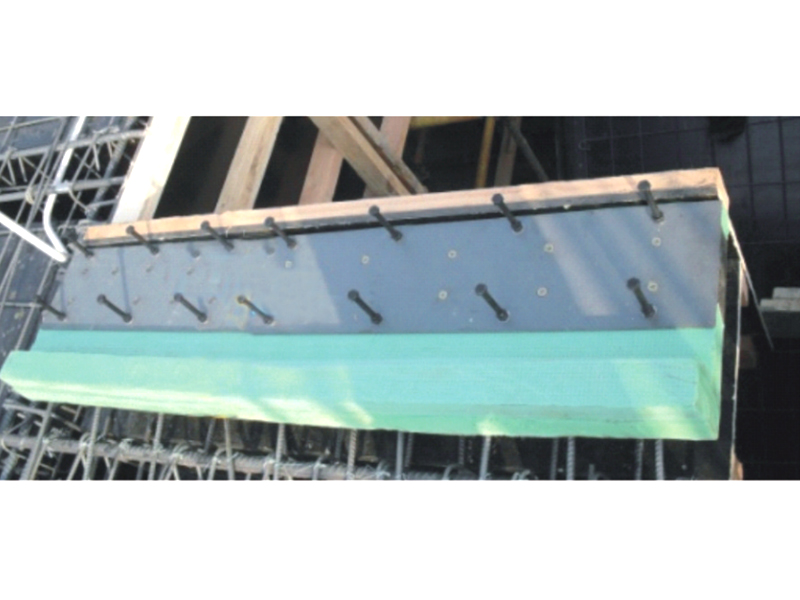
The fundamental design of a linear rubber bearing centers on its elastic properties. It typically consists of alternating layers of rubber and metal plates, bonded together under high pressure and temperature—a construction similar to some vibration isolators but optimized for linear guidance. The rubber layers allow for flexibility and shear deformation along the intended axis of movement, while the bonded metal plates provide structural integrity, distribute loads evenly, and prevent excessive bulging. This laminated structure grants the linear rubber bearing its unique ability to sustain substantial linear travel or offset under load while maintaining stiffness perpendicular to the direction of motion, serving as a combination of a guide and a flexible coupling.
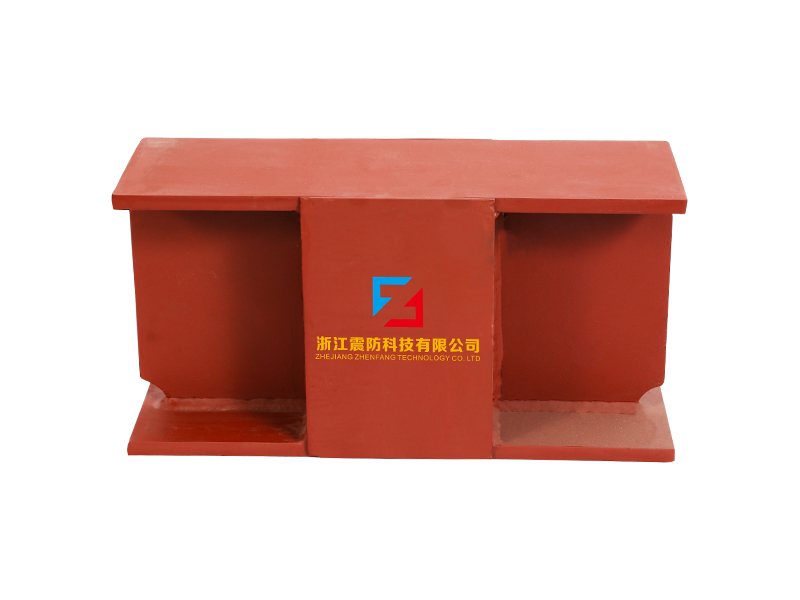
The operational role of a linear rubber bearing is crucial in applications where thermal expansion, misalignment compensation, or controlled linear movement must be managed without generating excessive friction or binding. A primary use is in pipe and duct support systems, particularly for large-diameter pipelines in power plants or industrial facilities. Here, the linear rubber bearing allows the pipeline to expand and contract longitudinally due to temperature changes while securely supporting its weight and restraining vertical and lateral movement. This prevents stress concentration at anchor points and reduces wear on pipe hangers, contributing to the system's long-term reliability.
Beyond piping, the linear rubber bearing finds important applications in precision machinery and transportation infrastructure. In manufacturing equipment, such as large presses or printing machines, these bearings can be used to guide platens or carriages, absorbing small misalignments and dampening vibrations to improve product quality and machine lifespan. Within bridge engineering, certain linear rubber bearing designs are employed at expansion joints or as part of seismic isolation systems for smaller spans, where they accommodate movement from traffic loads and temperature variations while providing a measure of damping. The inherent noise and vibration damping qualities of the rubber make the linear rubber bearing a favorable choice for applications where smooth, quiet operation is a priority.
The utilization of the linear rubber bearing is expected to grow alongside advancements in material science and simulation. The development of advanced rubber compounds with improved aging characteristics, wider temperature tolerance, and higher load capacity will expand the performance envelope of the linear rubber bearing. Furthermore, its role in modular and prefabricated construction techniques may increase, where managing tolerances and connections between large components is essential. As industries continue to seek solutions for managing movement, reducing maintenance, and isolating vibration in linear applications, the linear rubber bearing stands out as an elegant and effective solution, demonstrating how tailored elastomeric technology can solve complex engineering challenges with simplicity and reliability.