The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEIn regions prone to seismic activity, the paradigm of structural engineering is shifting from rigid resistance to managed flexibility, with the seismic isolation bearing emerging as a transformative technology. This specialized component is installed at the base of a structure or between key structural elements, serving as a flexible interface that decouples the building or bridge from the violent horizontal ground motions of an earthquake. By absorbing and dissipating seismic energy, the seismic isolation bearing significantly reduces the forces transmitted to the superstructure, protecting both the integrity of the construction and the lives of its occupants.
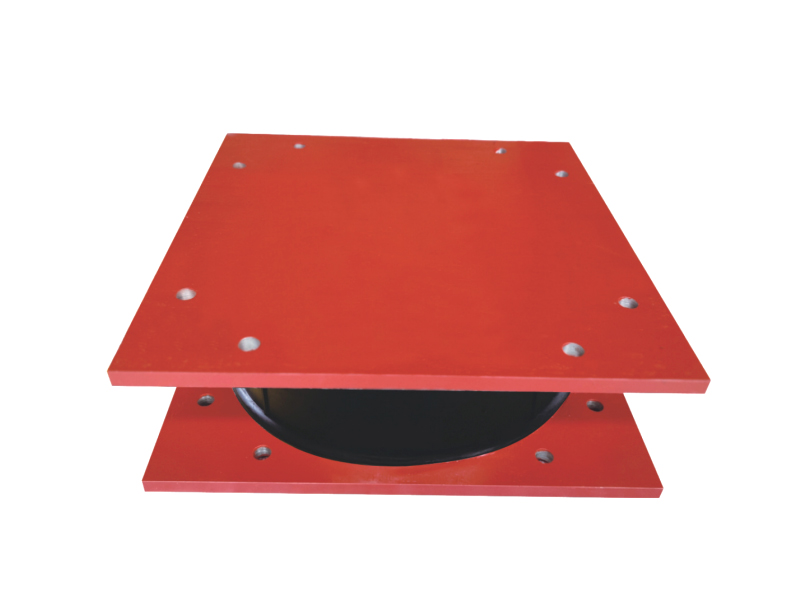
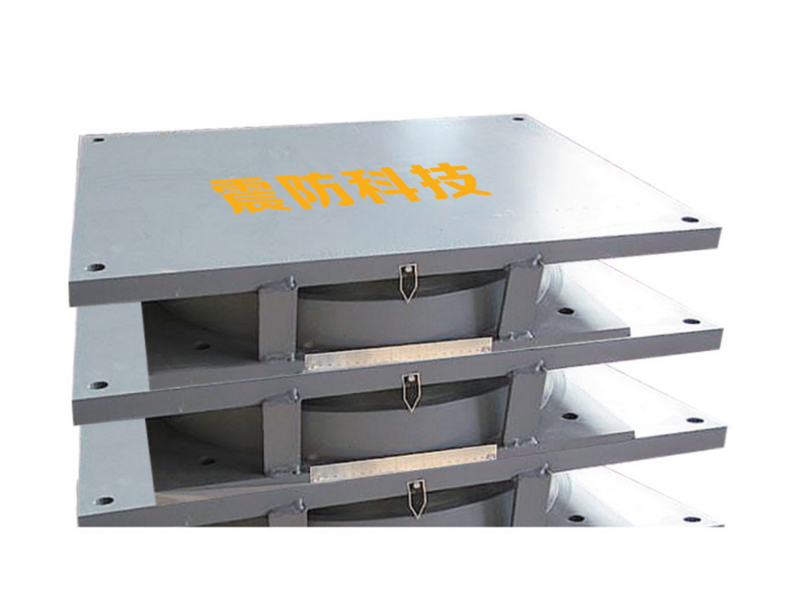
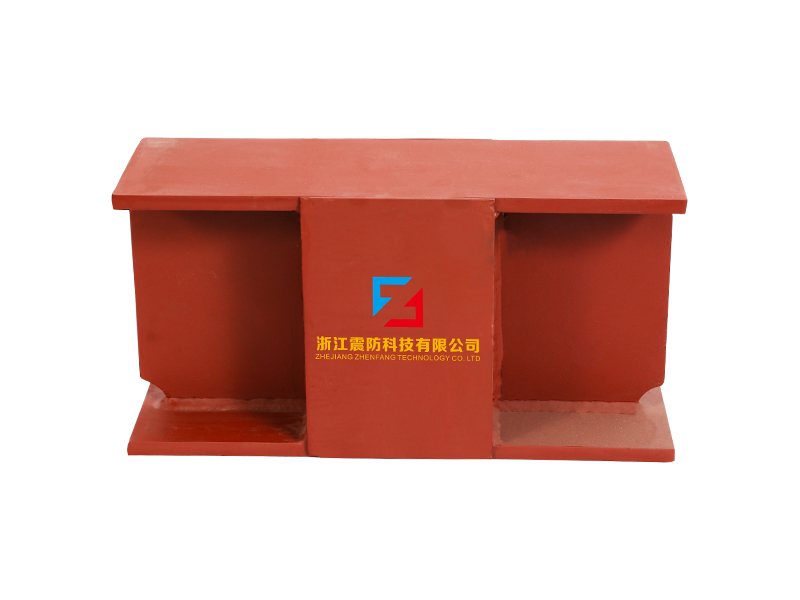
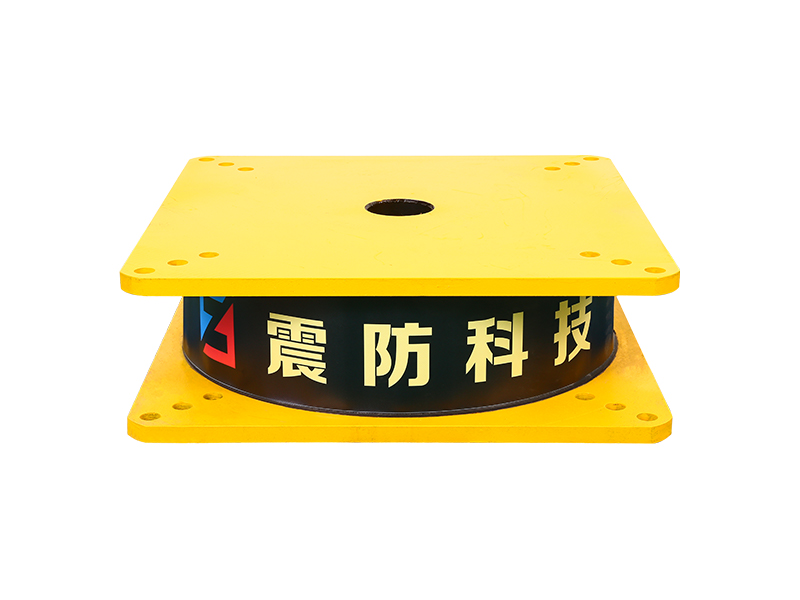
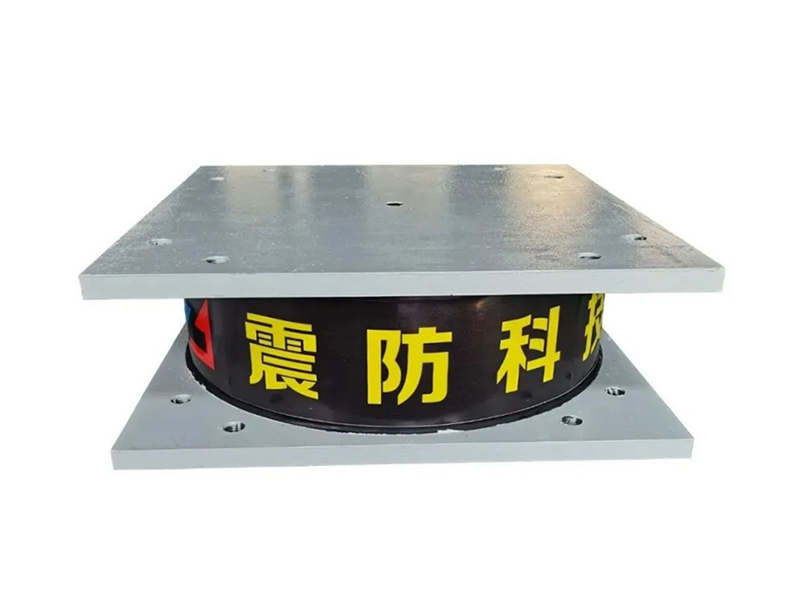
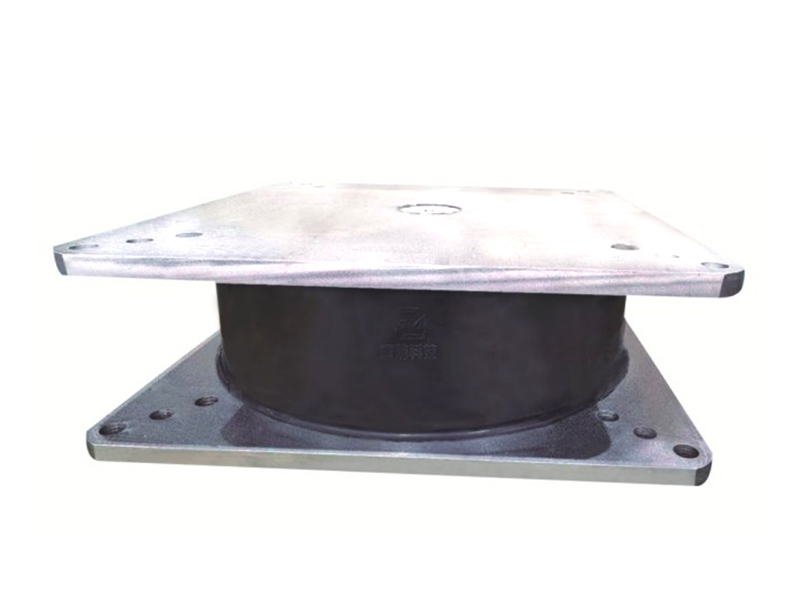
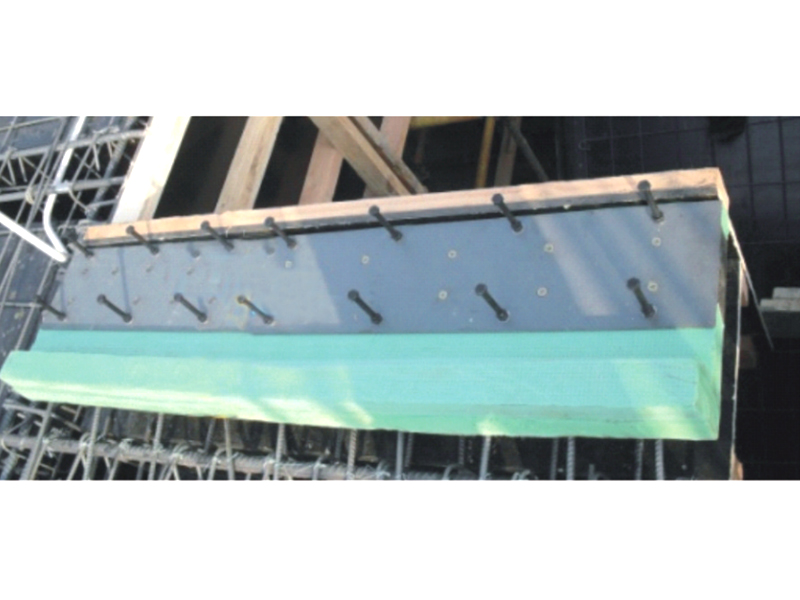
The core function of a seismic isolation bearing is to elongate the natural period of vibration of the structure and provide added damping. During an earthquake, the ground shakes at certain frequencies. A conventional fixed-base building will resonate with these frequencies, amplifying the shaking and stress. A seismic isolation bearing, however, introduces a layer of flexibility. Common types include elastomeric bearings (layers of rubber and steel) and sliding bearings with friction pendulum systems. This isolation layer allows the ground to move beneath the structure while the superstructure above sways gently and slowly—with a much longer period—experiencing dramatically reduced accelerations and inertial forces. This fundamental shift in dynamic response is the key advantage provided by the seismic isolation bearing.
The design and composition of a seismic isolation bearing are critical to its performance. High-damping rubber bearings incorporate specially compounded rubber that inherently dissipates energy as heat. Lead-rubber bearings have a central core that yields plastically to provide damping. Friction pendulum systems use a spherical sliding surface to achieve isolation and damping through friction. Each seismic isolation bearing is precisely engineered for the specific weight, geometry, and seismic hazard of the structure it supports. Rigorous prototyping and testing, often on large-scale shake tables, validate the performance of each seismic isolation bearing design under simulated earthquake forces.

The application of seismic isolation bearing technology is prominent in critical and high-occupancy structures. It is increasingly specified for hospitals, emergency response centers, data centers, and museums where functionality must be maintained after a seismic event. Bridges utilize seismic isolation bearing units to protect piers and decks, while the technology is also being applied to retrofit historic buildings and to protect sensitive equipment within industrial facilities. By implementing a seismic isolation bearing system, the design focus shifts from preventing collapse to ensuring immediate occupancy and continued operation post-earthquake, a standard known as "functional recovery."
Innovation in seismic isolation bearing technology focuses on enhanced durability, adaptive systems, and broader accessibility. Research includes developing new elastomeric compounds with improved aging characteristics and higher damping, as well as "smart" bearings with sensors to monitor their health and performance in real-time. There is also a push to develop lower-cost isolation solutions to make the technology viable for a wider range of buildings, including residential construction. As building codes evolve to emphasize resilience, and as climate change potentially influences seismic risks, the seismic isolation bearing is poised to transition from a specialized solution for critical infrastructure to a more widely adopted cornerstone of safer, more resilient communities in earthquake zones worldwide.