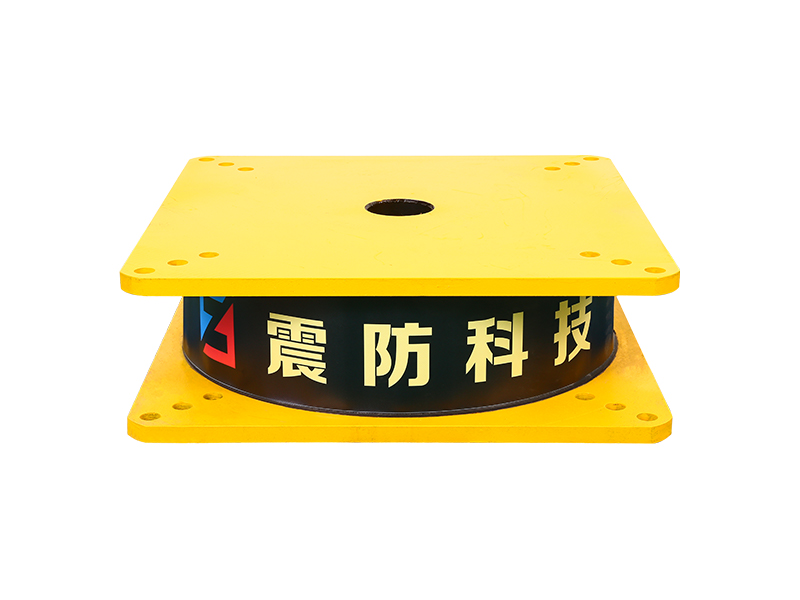
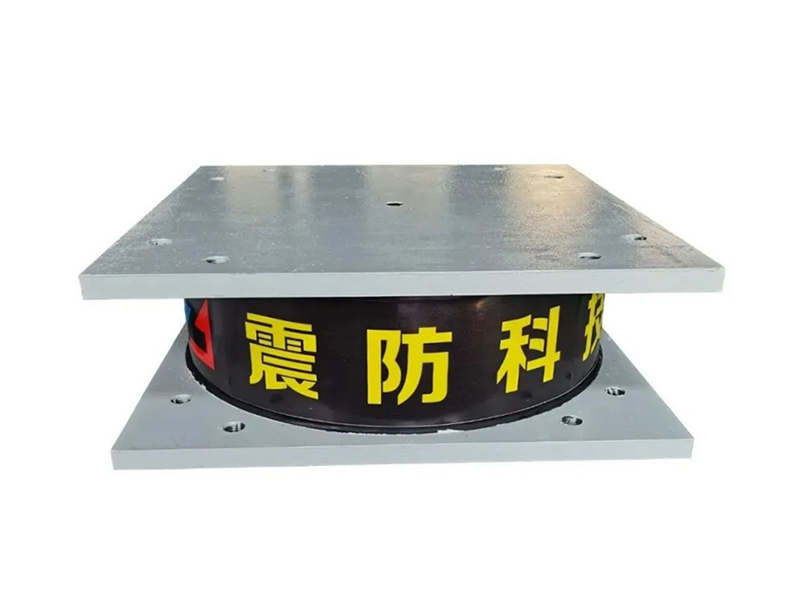
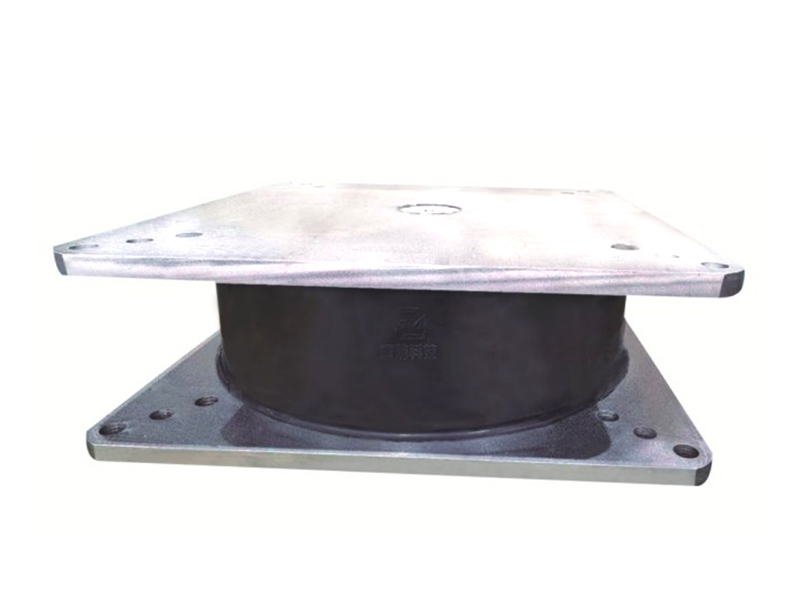
The basic characteristics of viscous fluid dampers are: Dissipation of energy, Design and Construction, Applications. In this article we will cover these topics and more. Ultimately, this article will assist you in selecting the best damper for your application. This article will be of interest to anyone involved in fluid flow or energy management. There are many uses for viscous fluid dampers in both the industrial and commercial sectors.
Dissipation of energy
If you're looking for a reliable, cost-effective viscous damper, there are several things you should know. For starters, the maximum forces and velocities that a viscous fluid damper can handle are difficult to predict. This means that you may need to optimize the design of your damper to minimize potential damage to your structure. If you're unsure of how to design a viscous damper, there are some simulation tools available.
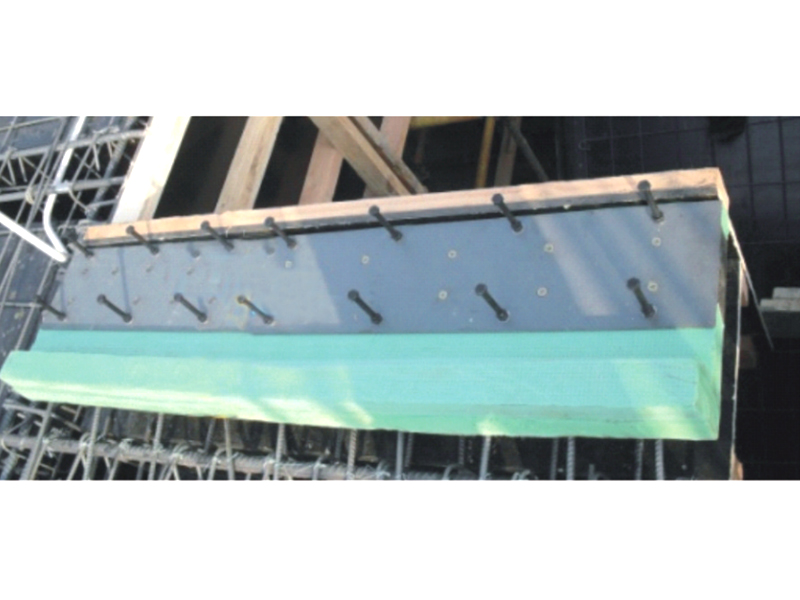
A viscous fluid damper is an effective solution for reducing the overall structural stiffness of a structure. They provide superior damping and reduce stress while still allowing the structure to be elastic. In practice, they are widely used in many fields, but the primary problem with them is the risk of oil leakage. There are also significant sealing issues with these dampers. Despite these drawbacks, these dampers have been used in hundreds of engineering applications.
Design
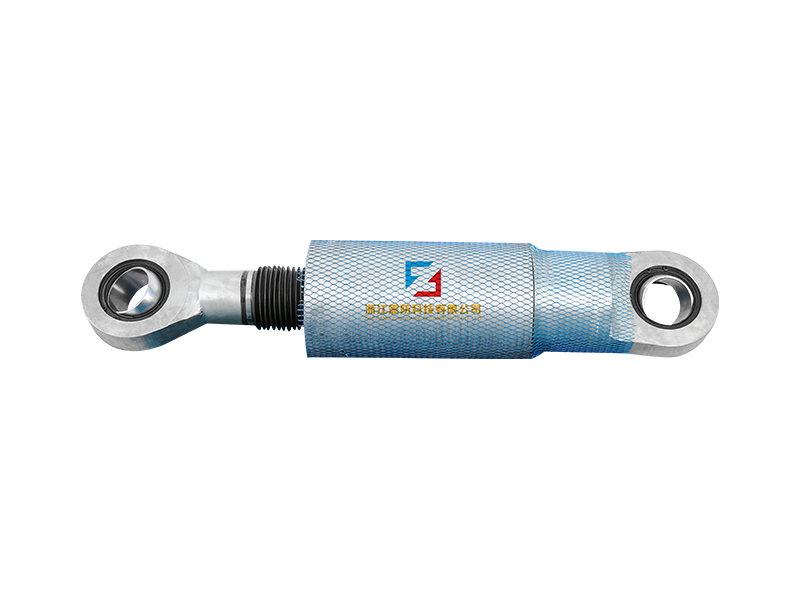
A viscous fluid damper is a device that can be used to control the torsional forces on a structure. Typically, this type of damper consists of a cylindrical body that resists structural motion with a force proportional to velocity. The viscous damper is used in seismic applications to reduce the amount of shock and vibration felt by a structure. Several different damper designs exist, and this article will discuss the differences between them.
The viscous damper is measured by using a transducer directly placed on the device. The applied loading history is shown in Figure 15.2. The measured displacement time history is then used to calculate the acceleration and velocity records. After that, the data are subjected to wavelet-based denoising. The resultant forces are compared to those measured with conventional viscous dampers, and a comparison between the two types of damper is made.
Construction
A viscous fluid damper is a type of earthquake-dampening device that dampens the vibration of a structural member, pipe, or tank. The dilatant fluid demonstrates great resistance to motion as the speed of the motion increases. This is because the shoulder surfaces of the damper are rounded and the dilatant fluid is viscous, making it difficult for the motion to cause damage to the structure.
A VE damper is designed to dissipate vibration in a wide range of temperatures. VE dampers are commonly used for vibration mitigation in civil engineering structures. Their design allows them to be adapted to a variety of applications, including seismic monitoring and seismic protection systems. Because they are highly sensitive to temperature, testing them extensively is critical to ensure that they work in the most difficult conditions. Listed below are the main benefits of a VE damper.
Applications
VE dampers are widely used in various civil engineering structures. The ideal linear damper opposes structural motion with a force proportional to velocity. The cylinder can be mounted directly on the steel or connected to a foundation block in the ground. The cylinder is a reusable component for the entire building. A VE damper's performance is also affected by the type of mounting system it is used in.
Unlike springs, viscous fluids move slowly. When exposed to shear, they will move, but only when the resistance is too great to remain. The resulting movement generates heat, which must be removed to avoid damaging equipment. For this reason, dampers designed to resist this heat often include heat sinks or radiator fins. Air can also be used to cool large dampers. In addition, the efficiency of viscous dampers is greatly affected by the amount of heat they generate.
Impact of COVID-19 on the global economy
The Viscous Fluid Damper Market Research study includes a number of factors to help determine the size of this market. The study examines the demand and supply of this product by region and end-user. It includes the historical market data and future forecast for the market, which provides a holistic view of various economic factors. The report also highlights emerging niche segments in the market. This study will help investors understand the market potential and identify lucrative growth opportunities in the coming years.