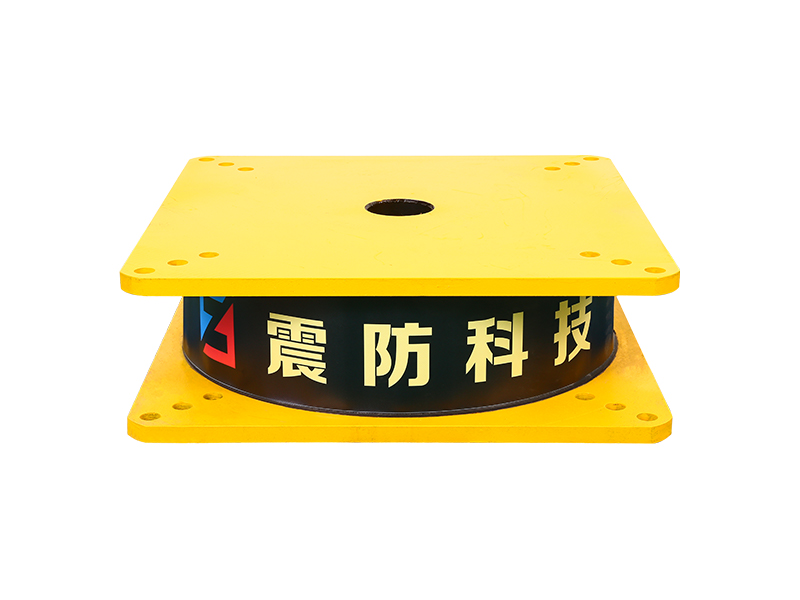
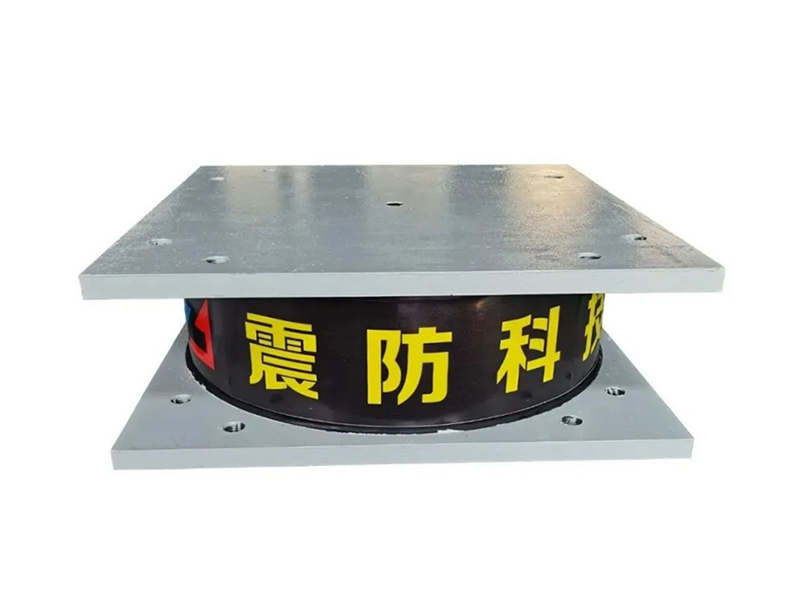
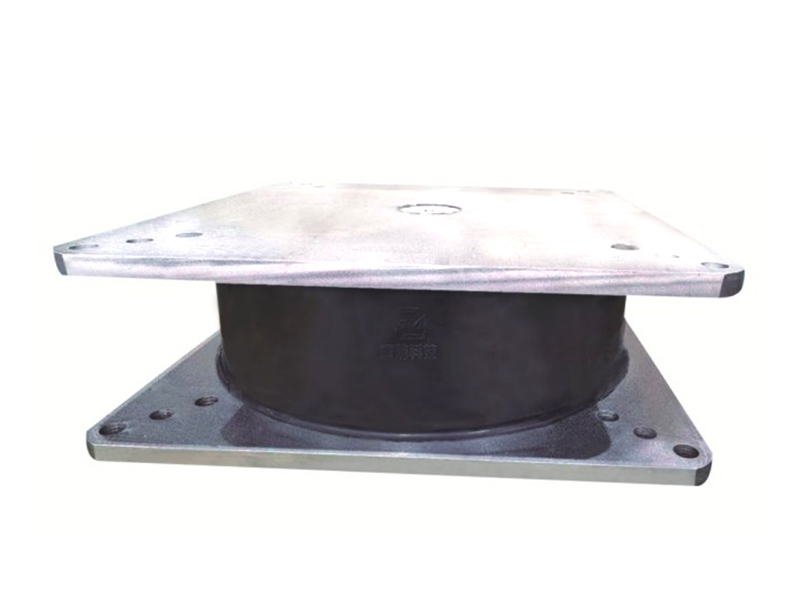
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEIn regions prone to seismic activity, the pursuit of earthquake-resilient infrastructure has led to the widespread adoption of a sophisticated isolation technology: the lead rubber bearing. This specialized device is engineered to be installed at the base of structures, such as buildings and bridges, where it serves a dual protective function. The lead rubber bearing effectively decouples the superstructure from the damaging horizontal motions of the ground during an earthquake, significantly enhancing safety and reducing structural damage.
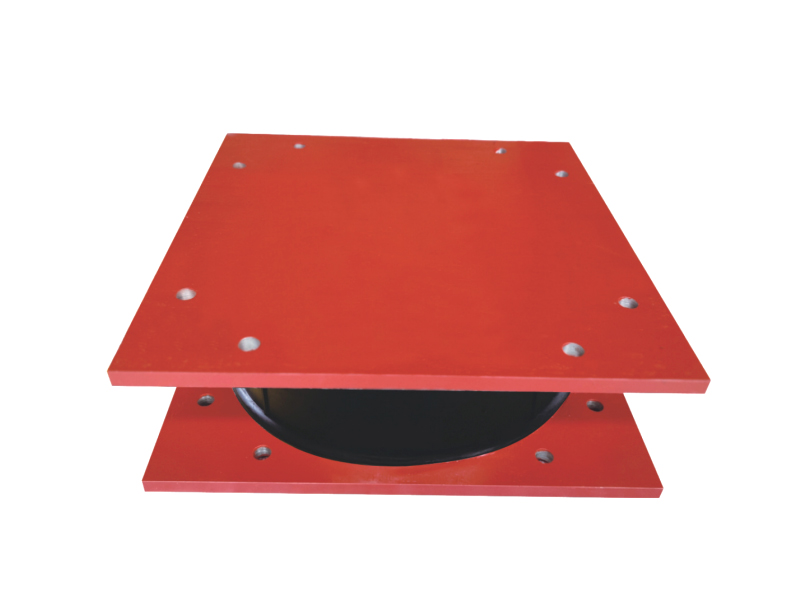
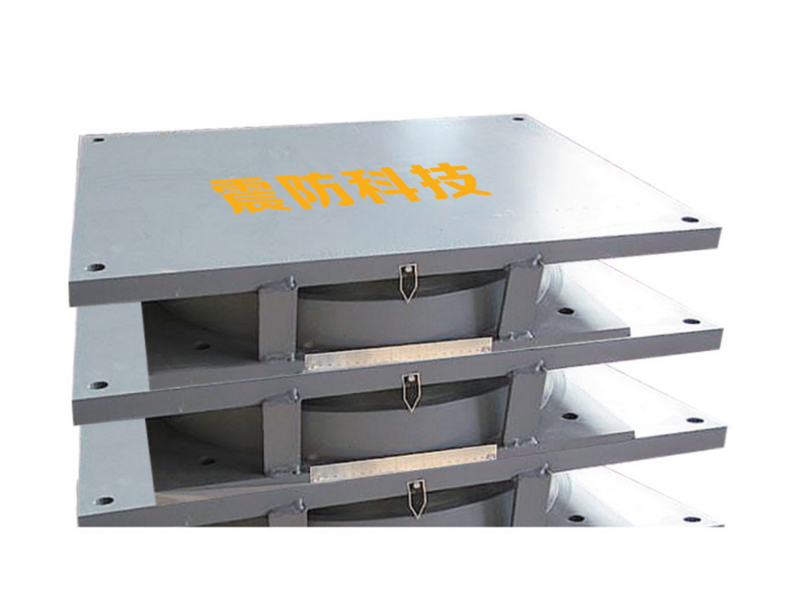
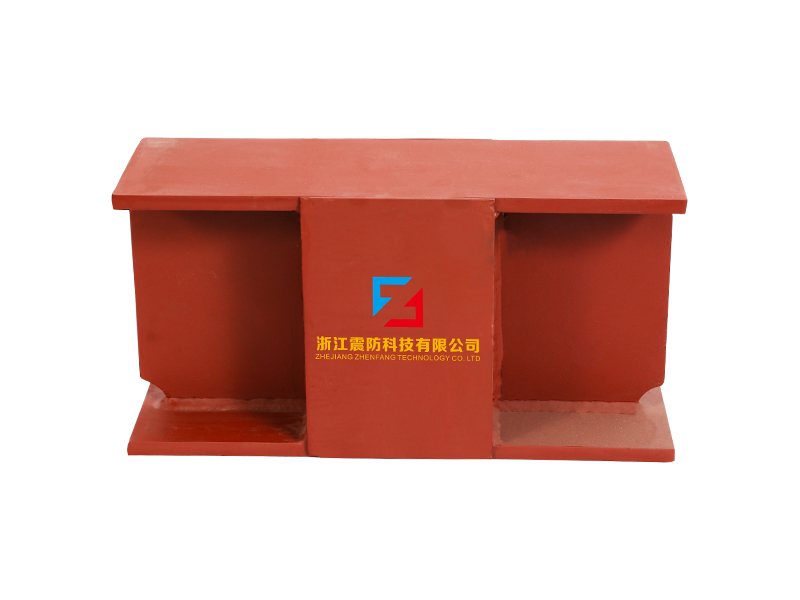
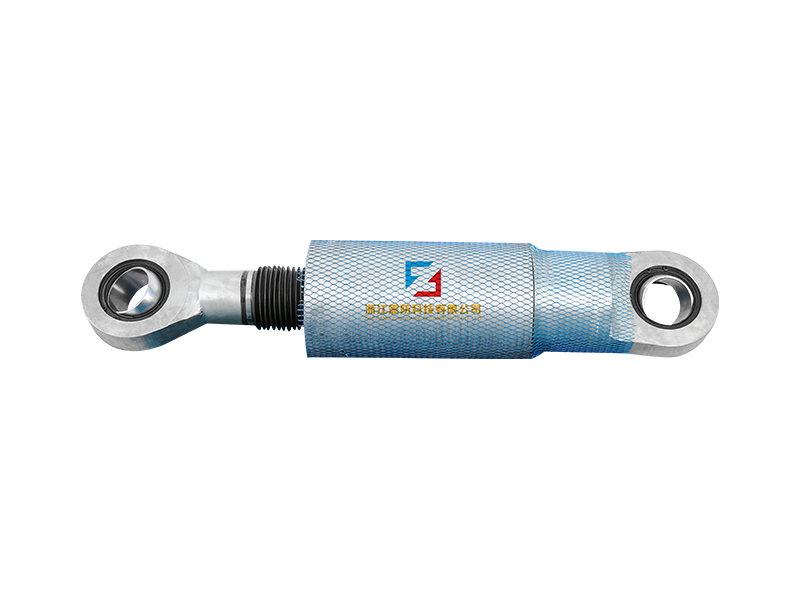
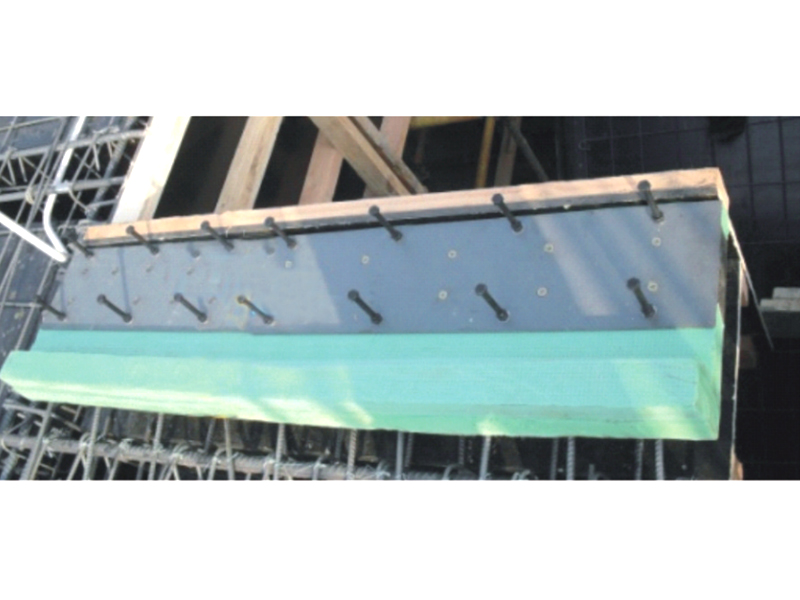
The design of a standard lead rubber bearing is elegantly purposeful. It consists of multiple layers of rubber and steel plates bonded together, with a solid lead core inserted at the center. The laminated rubber and steel plates provide vertical stiffness to support the weight of the structure while allowing for considerable horizontal flexibility. This flexibility is the key to isolation, permitting the building or bridge deck to sway slowly and independently from the rapid shaking of the ground below. The integrated lead core is the second critical element; it offers energy dissipation through its ability to yield plastically. As the lead rubber bearing deforms during seismic motion, the lead core absorbs and dissipates a substantial amount of the earthquake's energy as heat, damping the vibrations of the isolated structure.
The primary advantage offered by a well-designed lead rubber bearing system is the drastic reduction in seismic forces transferred to the structure. Traditional fixed-base buildings are forced to follow every movement of the ground, pilot to high internal stresses. In contrast, a structure mounted on lead rubber bearing units experiences a slower, filtered motion. This can lower the effective seismic forces by a considerable margin, protecting critical structural elements and non-structural components like facades, partitions, and machinery. The application of lead rubber bearing technology is considered a form of passive base isolation, a proven strategy for safeguarding hospitals, data centers, historic landmarks, and essential bridges.

The performance and reliability of a lead rubber bearing are subject to rigorous testing and standardization. Prototypes undergo extensive dynamic testing to verify their force-displacement characteristics, energy dissipation capacity, and long-term durability. Engineers must carefully calculate the required properties of each lead rubber bearing—including its diameter, total rubber thickness, and lead core size—based on the specific weight, geometry, and seismic hazard at the construction site. Quality control in the manufacturing of the lead rubber bearing is paramount, as the integrity of the rubber-to-steel bonding and the consistency of the lead core are essential for dependable performance over decades.
Installation of a lead rubber bearing system is a precise engineering undertaking. The bearings are typically placed on top of foundation piers or basement columns, with the superstructure constructed above them. Construction sequences must account for the initial flexibility before the structure is completed. Maintenance generally involves regular visual inspections to check for any signs of deterioration, though the lead rubber bearing itself is designed as a long-life, low-maintenance component within the structural system.
The role of the lead rubber bearing is set to remain crucial as urbanization continues in earthquake-prone areas and as societies prioritize disaster resilience. The technology also holds promise for the seismic retrofit of existing vulnerable structures. By providing a predictable and reliable means of protecting both infrastructure and human life, the lead rubber bearing stands as a foundational innovation in modern civil engineering, demonstrating how intelligent material science can be applied to mitigate the forces of nature.