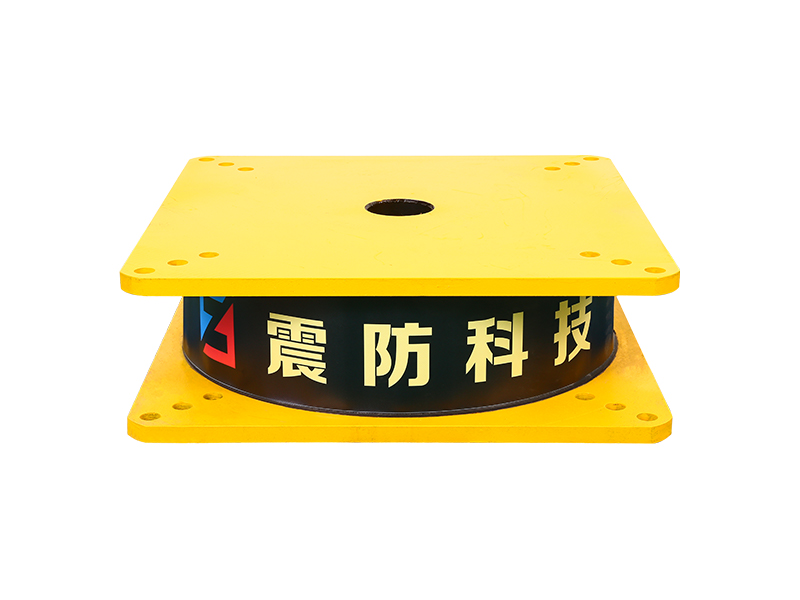
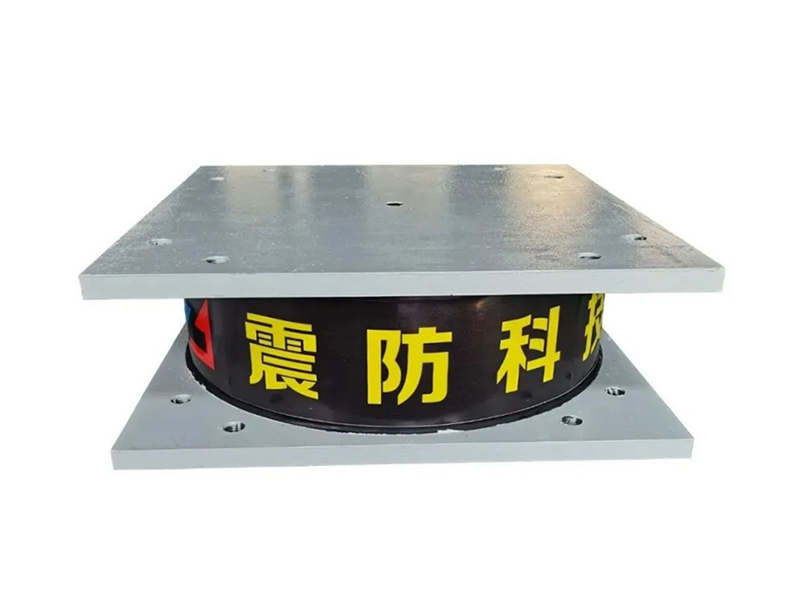
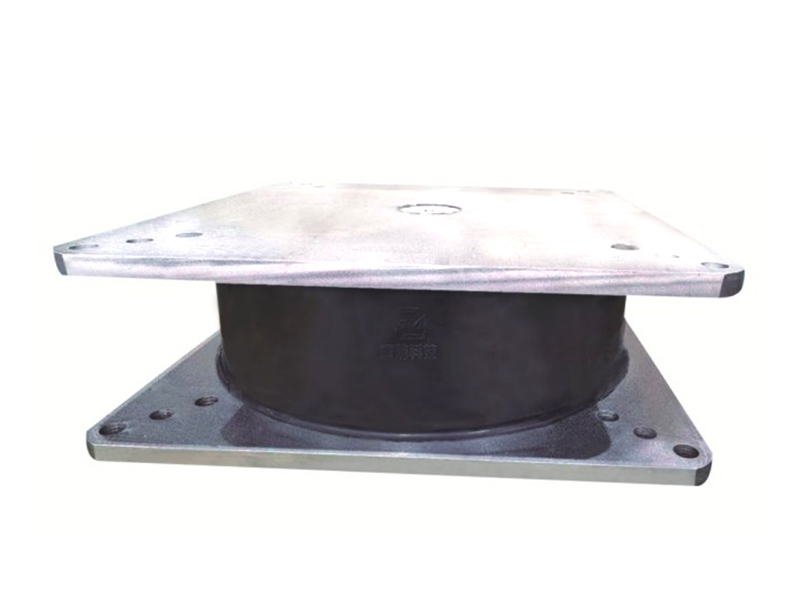
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEA specialized component known as the linear rubber bearing is finding increased application in various industries where controlled, low-friction linear motion is required alongside vibration damping and noise reduction. Unlike traditional rigid linear ball bearings or bushings, the linear rubber bearing incorporates a flexible elastomeric element within its design. This unique construction allows the linear rubber bearing to accommodate minor misalignments, absorb shock, and operate quietly, making it a valuable solution for specific engineering challenges in automation, transportation, and precision equipment.
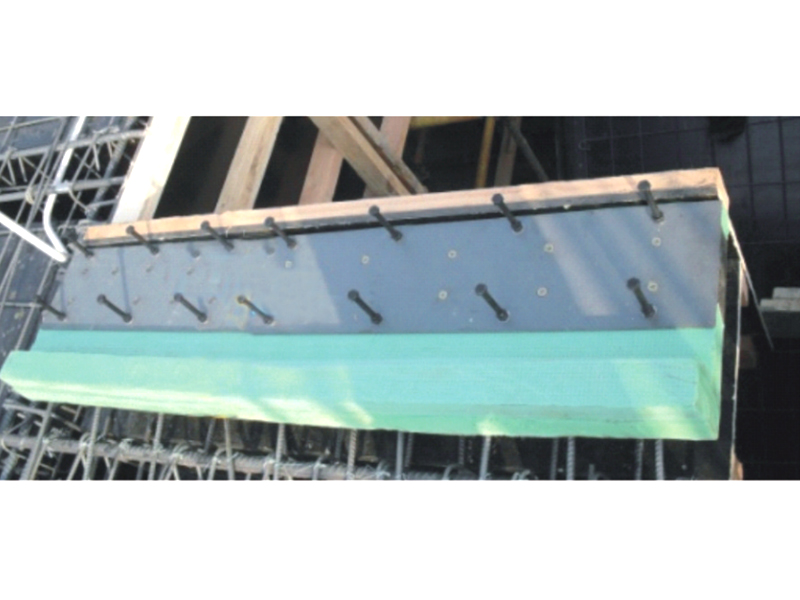
The fundamental design of a linear rubber bearing typically involves a metal sleeve or housing that contains a cylindrical lining made of a engineered rubber compound. A polished metal shaft, often stainless steel, moves within this rubber-lined bore. The elasticity of the rubber material in the linear rubber bearing provides several distinct functional advantages. It creates a damped, smooth motion profile, reduces the transmission of structure-borne noise and vibration, and compensates for small angular or parallel misalignments between the shaft and the housing that would cause binding or rapid wear in a purely metallic bearing system. This inherent flexibility is the core value proposition of the linear rubber bearing.
The operational benefits of the linear rubber bearing make it suitable for a range of applications. In automotive and vehicle subsystems, the linear rubber bearing is often employed in throttle linkages, gear shift mechanisms, and seat adjustment rails, where it ensures smooth operation while isolating vibration from the passenger compartment. Within industrial automation, the linear rubber bearing can be found in certain conveyor system guides, packaging machinery actuators, and assembly station slides, particularly in environments where quiet operation is beneficial. The ability of the linear rubber bearing to function with small lubrication or even dry makes it attractive for use in clean environments or with sensitive products.
Compared to other linear motion components, the selection of a linear rubber bearing involves specific considerations. While it offers outstanding damping and misalignment tolerance, a linear rubber bearing generally has a lower load capacity and a more limited up to speed than a recirculating ball bearing. Its performance is also sensitive to temperature and the chemical compatibility of the rubber compound with the operating environment. Therefore, engineers specify a linear rubber bearing primarily in situations where its unique damping and flexibility characteristics are required, and where motion parameters like speed and load are within its effective range. Proper shaft hardness and surface finish are also critical for the long-term performance of a linear rubber bearing.
The niche for the linear rubber bearing appears well-defined and growing in specific sectors. Its role is particularly relevant as industries seek to improve the acoustic performance and smoothness of consumer-facing mechanisms and to solve alignment issues in complex assemblies. Future advancements may cause linear rubber bearing designs with hybrid materials or integrated sensors for condition monitoring. While not a universal replacement for all linear guides, the linear rubber bearing stands as a testament to the value of incorporating flexible, damping elements into motion systems. Its continued use and refinement highlight an important engineering principle: that ideal performance often comes from a component that not only guides motion but also intelligently manages the forces and imsuperbions inherent in real-world mechanical systems.