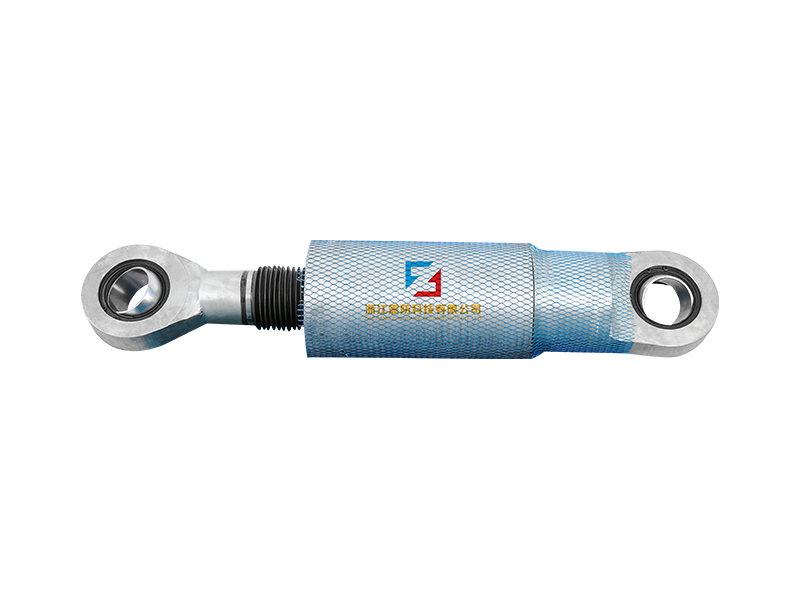
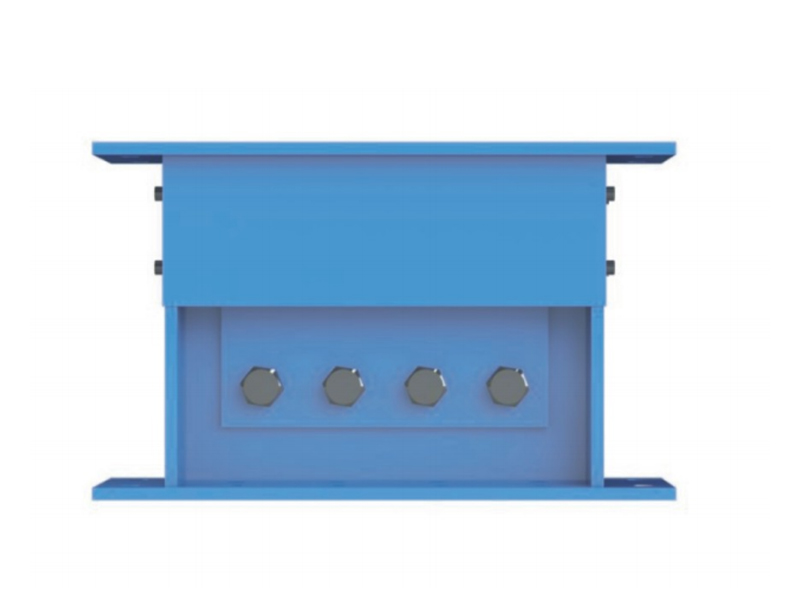
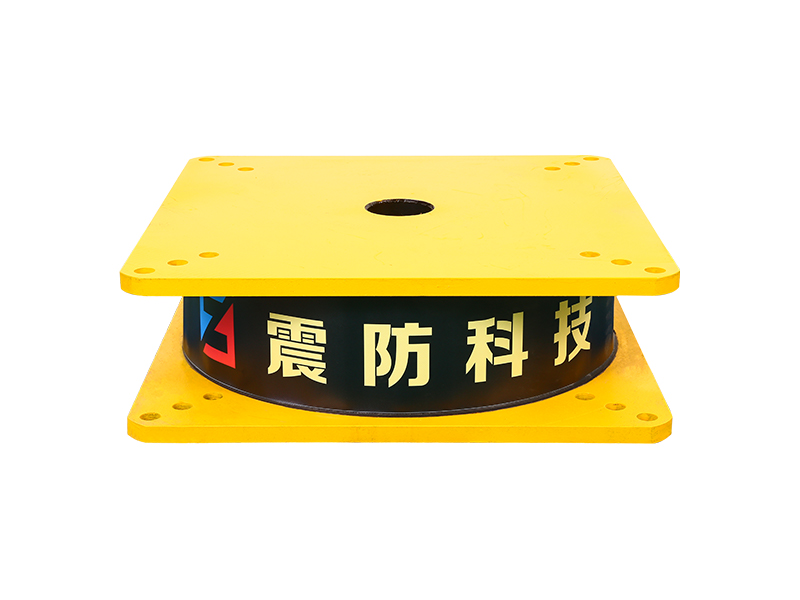
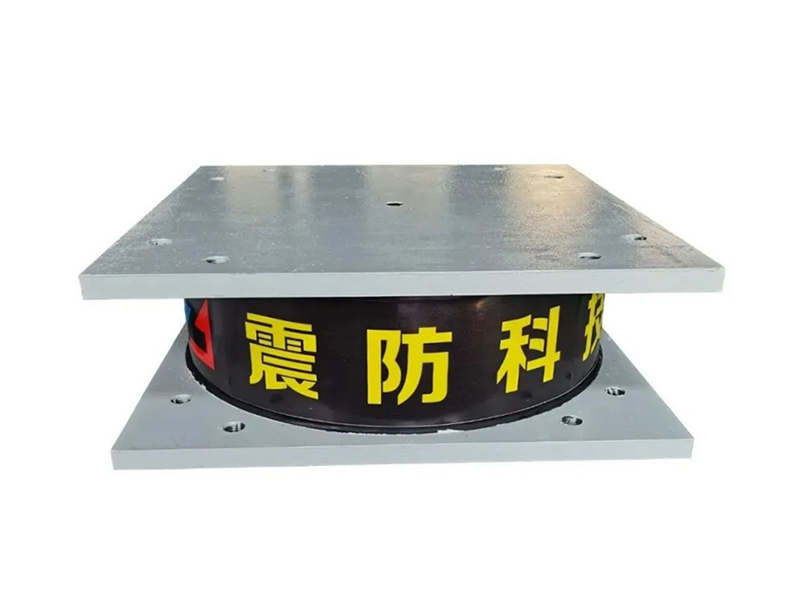
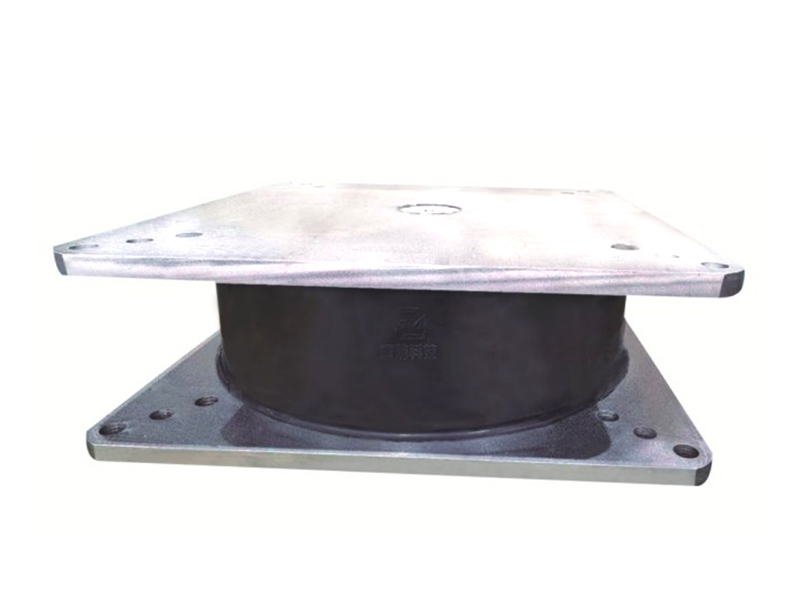
The company has been adhering to the corporate tenet of "quality first, customer first", and sincerely welcomes domestic and foreign customers to visit and guide.
GET A QUOTEThe component known as the metal damper is attracting renewed interest for its role in managing vibration, absorbing shock, and dissipating energy across a diverse range of engineering fields. Unlike damping systems that rely on viscoelastic polymers or hydraulic fluids, the metal damper utilizes the inherent hysteresis and plastic deformation of specific metallic materials or assemblies to convert mechanical energy into heat. This approach offers distinct advantages in terms of durability, performance stability across temperature ranges, and structural integration, prompting engineers to reconsider the metal damper for both traditional and innovative applications.
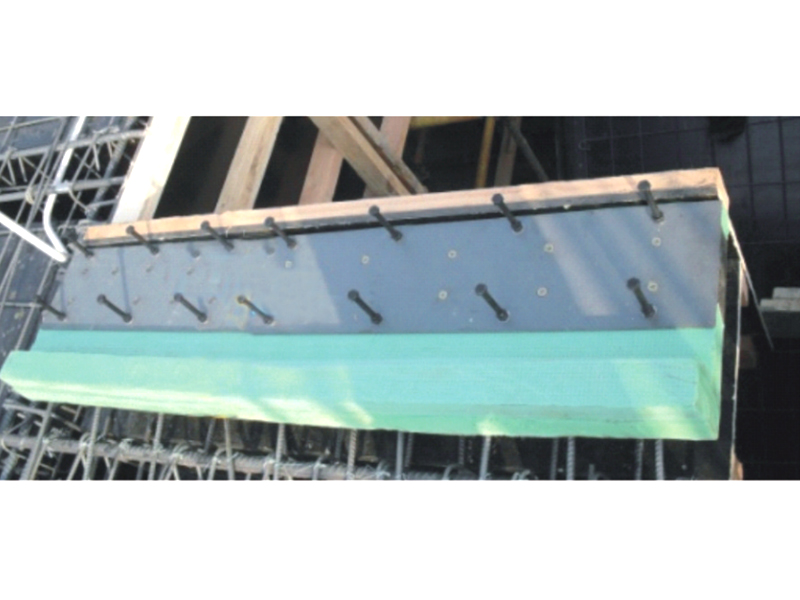
The fundamental operating principle of a metal damper is based on the inelastic deformation of metal elements. Common designs include friction-based metal damper systems, where sliding between metal surfaces under controlled pressure dissipates energy, and yielding-type metal damper units, which use the targeted plastic deformation of metals like mild steel or shape-memory alloys. When a structure or component experiences dynamic forces, the metal damper activates, undergoing cyclic deformation. This process effectively absorbs kinetic energy that would otherwise translate into excessive motion, vibration, or structural stress, thereby improving stability and comfort or protecting sensitive equipment.
One of the many established and critical applications for the metal damper is in civil and structural engineering, particularly in seismic regions. Here, specialized metal damper devices are integrated into the frames of buildings and bridges. During an earthquake, these structural metal damper units are designed to yield or slide in a controlled manner, absorbing a significant portion of the seismic energy. This action helps to protect the primary load-bearing members of the structure from damage, enhancing overall safety. The robust and predictable performance of a well-designed metal damper under bad conditions is a key reason for its adoption in seismic retrofit projects and new construction designed for resilience.
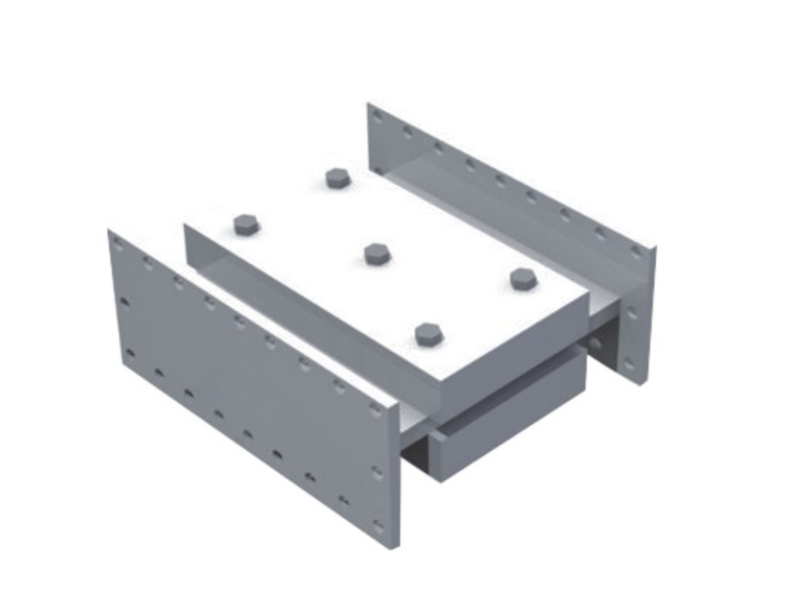

Beyond seismic protection, the utility of the metal damper extends into mechanical and industrial systems. In automotive and transportation sectors, various forms of metal damper are employed in suspension components, drivetrain mounts, and even within certain types of crash boxes to manage impact forces. In the realm of precision manufacturing and aerospace, compact metal damper devices can be used to stabilize machinery, suppress chatter in machining processes, or isolate sensitive instruments from ambient vibration. The ability of a metal damper to perform consistently in high-temperature environments where organic dampers would degrade is a notable advantage in these technical fields.
The development of the metal damper is closely linked to advancements in materials science and simulation technology. Engineers can now design metal damper devices with greater precision, using computer modeling to predict their hysteretic behavior and fatigue life. Research continues into new alloys and composite metallic systems that offer ideal combinations of strength, ductility, and energy dissipation capacity for the metal damper.
The potential applications for metal damper technology are likely to expand. Trends in lightweight construction and the need to protect infrastructure and machinery from increasingly dynamic loads, including wind and operational vibrations, will drive further innovation. As the demand for solutions that enhance safety, durability, and performance grows across industries, the metal damper, with its blend of mechanical simplicity and robust effectiveness, is poised to remain a vital tool in the engineer's portfolio for managing energy and motion in the built and mechanical environment.